Protein lipidation in the tumor microenvironment: enzymology, signaling pathways, and therapeutics
- PMID: 40335986
- PMCID: PMC12057185
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-025-02309-7
Protein lipidation in the tumor microenvironment: enzymology, signaling pathways, and therapeutics
Abstract
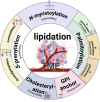
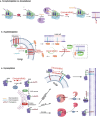
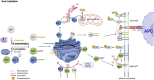
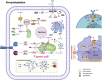
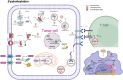
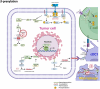
Protein lipidation is a pivotal post-translational modification that increases protein hydrophobicity and influences their function, localization, and interaction network. Emerging evidence has shown significant roles of lipidation in the tumor microenvironment (TME). However, a comprehensive review of this topic is lacking. In this review, we present an integrated and in-depth literature review of protein lipidation in the context of the TME. Specifically, we focus on three major lipidation modifications: S-prenylation, S-palmitoylation, and N-myristoylation. We emphasize how these modifications affect oncogenic signaling pathways and the complex interplay between tumor cells and the surrounding stromal and immune cells. Furthermore, we explore the therapeutic potential of targeting lipidation mechanisms in cancer treatment and discuss prospects for developing novel anticancer strategies that disrupt lipidation-dependent signaling pathways. By bridging protein lipidation with the dynamics of the TME, our review provides novel insights into the complex relationship between them that drives tumor initiation and progression.
Keywords: N-myristoylation; S-palmitoylation; S-prenylation; Lipidation; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

