Emerging nanotechnologies and their role in early ovarian cancer detection, diagnosis and interventions
- PMID: 40336114
- PMCID: PMC12057071
- DOI: 10.1186/s13048-025-01678-3
Emerging nanotechnologies and their role in early ovarian cancer detection, diagnosis and interventions
Abstract
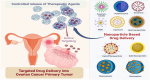
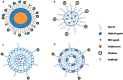
Ovarian cancer presents a significant public health challenge, often being diagnosed at advanced stages due to the limitations of current detection methods. This systematic review addresses the urgent need for innovative approaches to enhance early detection and diagnosis of ovarian cancer. We systematically evaluate recent advancements in nanotechnology, focusing specifically on their novel applications and potential in comparison to traditional diagnostic modalities. Our analysis encompasses a wide range of studies investigating nanoparticles, biosensors, advanced imaging techniques, and biomarker detection platforms, with an emphasis on evaluating key performance indicators such as detection rates, turnaround times, and the accuracy of distinguishing cancerous from non-cancerous tissues. Our findings indicate that nanotechnology-based approaches have the potential to significantly improve early detection capabilities for ovarian cancer. Notably, studies on nanoparticle-based imaging techniques and biosensors consistently demonstrate high sensitivity and specificity for identifying ovarian cancer biomarkers, with detection rates exceeding 90% reported for early-stage cancers in several instances. This review underscores the promise of emerging nanotechnologies to transform the landscape of early detection and diagnosis, offering a pathway toward earlier diagnoses, enhanced therapeutic interventions, and improved patient outcomes. We advocate for future research dedicated to the translational efforts required to move these technologies from bench to bedside, ensuring their effectiveness is validated across diverse clinical populations.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Biosensors; Imaging techniques; Nanocarriers; Nanoparticles; Ovarian cancer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potentials of MicroRNA in Early Detection of Ovarian Cancer by Analytical Electrical Biosensors.Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2022;52(7):1511-1523. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2021.1890543. Epub 2021 Jun 7. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2022. PMID: 34092138 Review.
-
Nanotechnology: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(19):1-43. Epub 2006 Nov 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074489 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in surface plasmon resonance for the detection of ovarian cancer biomarkers: a thorough review.Mikrochim Acta. 2024 Oct 9;191(11):659. doi: 10.1007/s00604-024-06740-3. Mikrochim Acta. 2024. PMID: 39382786 Review.
-
Modern Emerging Biosensing Methodologies for the Early Diagnosis and Screening of Ovarian Cancer.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Mar 21;15(4):203. doi: 10.3390/bios15040203. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40277517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in protein glycosylation biomarkers for ovarian cancer through mass spectrometry-based approaches.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2024 Apr;24(4):249-258. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2023.2297933. Epub 2023 Dec 25. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2024. PMID: 38112537 Review.
Cited by
-
The Application of Functional Nanomaterials-Based Electrochemical Biosensors in Detecting Cancer Biomarkers: A Review.Molecules. 2025 Jun 23;30(13):2708. doi: 10.3390/molecules30132708. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40649227 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gupta KK, Gupta VK, Naumann RW. Ovarian cancer: screening and future directions. Int J Gynecologic Cancer. 2019;29(1). - PubMed
-
- Al-Thani AN, Jan AG, Abbas M, Geetha M, Sadasivuni KK. Nanoparticles in cancer theragnostic and drug delivery: A comprehensive review. Life Sci. 2024 Jul;9:122899. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

