Lapdoctor: Multicentre Validation of a Scoring System for Preoperative Evaluation of Difficulty of Laparoscopic Donor Nephrectomy
- PMID: 40336540
- PMCID: PMC12055550
- DOI: 10.3389/ti.2025.14100
Lapdoctor: Multicentre Validation of a Scoring System for Preoperative Evaluation of Difficulty of Laparoscopic Donor Nephrectomy
Abstract
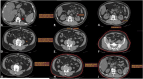
We previously developed and validated LAPDOCTOR (LAParoscopic-Donor-nephreCTomy-scORe), a novel scoring system for the preoperative assessment of the difficulty of living donor nephrectomy (LDN). To prove its significance, we extended our investigation to a prospective, multicenter, national study. Difficulty was assessed by the operating surgeon using a scale from 1 to 3 (1-standard, 2-moderately difficult, 3-very difficult) based on eight parameters: availability of laparoscopic space, mobilization of the colon, kidney, gonadal, adrenal and renal vein, renal artery, and ureter. Donor CT-scans were blindly reviewed by a radiologist, and the LAPDOCTOR scores were compared with the difficulty levels assigned by the surgeon to investigate the match rates. One hundred eighty-five donors were enrolled, with a mean age of 54 years (range 24-77), BMI 25 kg/m2 (range 17-35), and male/female 59/126. LDN was blindly scored as standard in 45% of the cases, moderately-difficult in 52%, and very-difficult in 3%. The agreement between the LAPDOCTOR and expert donor surgeons' rate in categorizing LDN into risk groups had a QWK of 0.711 (95% CI 0.577-0.844) with p < 0.001. The LAPDOCTOR enables precise preoperative determination of the difficulty of LDN, particularly in very difficult cases, and assessment of surgical risk in living kidney donors.
Clinical trial notation: https://ClinicalTrials.gov, Identifier NCT05769686.
Keywords: laparoscopic donor nephrectomy score LDKT; living donor nephrectomy; minimal invasive; precision medicine; risk assessment.
Copyright © 2025 Romagnoli, Spagnoletti, Rossini, Iezzi, Posa, Salerno, Silvestri, Rossini, Silvestre, Franchin, Giacomoni, Centonze, Spada, Iaria, Puliatti and Furian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- OPTN National Data. (2024). Available online at: https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/data/view-data-reports/national-data/# (Accessed: April 10, 2024).
-
- Spagnoletti G, Romagnoli J. The Role of Mini-Invasive Approaches in Living Kidney Donation. Eur J Transplant (2024) 2(1):39–43. 10.57603/EJT-322 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

