New nicotinamide-thiadiazol hybrids as VEGFR-2 inhibitors for breast cancer therapy: design, synthesis and in silico and in vitro evaluation
- PMID: 40337008
- PMCID: PMC12056735
- DOI: 10.1039/d5ra01223f
New nicotinamide-thiadiazol hybrids as VEGFR-2 inhibitors for breast cancer therapy: design, synthesis and in silico and in vitro evaluation
Abstract
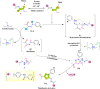
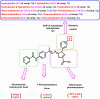
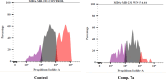
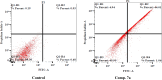
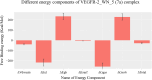
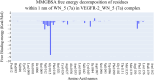
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) is a key regulator of tumor angiogenesis and has become an important target in anticancer drug development. In this study, novel nicotinamide-thiadiazol hybrids were synthesized and evaluated for their anti-breast cancer potential through VEGFR-2 inhibition. The compounds were assessed in vitro for their cytotoxicity against MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cell lines. Among the nicotinamide-thiadiazol hybrids, 7a exhibited the most potent anticancer activity, with IC50 values of 4.64 ± 0.3 μM in MDA-MB-231 and 7.09 ± 0.5 μM in MCF-7, showing comparable efficacy to sorafenib. VEGFR-2 inhibition assays confirmed strong inhibitory potential with an IC50 of 0.095 ± 0.05 μM. In vitro cell cycle analysis indicated that 7a induced S-phase arrest, while apoptosis assays demonstrated a substantial increase in late apoptotic cells (44.01%). Other in vitro mechanistic studies further confirmed the activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, as evidenced by caspase-3 activation (8.2-fold), Bax upregulation (6.9-fold), and Bcl-2 downregulation (3.68-fold). Computational studies, including molecular docking and 200 ns molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, confirmed the stable interaction of 7a with VEGFR-2, showing binding affinities comparable to sorafenib. Further validation through MM-GBSA, ProLIF, PCAT, and FEL analyses reinforced its strong binding capability. Additionally, ADMET predictions suggested favorable pharmacokinetic properties, including good absorption, high plasma protein binding, and non-CYP2D6 inhibition. Moreover, toxicity analysis classified 7a as non-mutagenic and non-carcinogenic, with a lower predicted toxicity than sorafenib. Finally, density functional theory (DFT) calculations highlighted the structural stability and reactivity of 7a, further supporting its potential as a VEGFR-2 inhibitor. These findings suggest that 7a is a promising VEGFR-2 inhibitor with significant anticancer potential, favorable pharmacokinetics, and an improved safety profile. Further preclinical studies and structural modifications are warranted to optimize its therapeutic potential.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures










References
-
- Schwartz S. M. Epidemiology of Cancer. Clin. Chem. 2024;70(1):140–149. - PubMed
-
- Shah A. A. Kamal M. A. Akhtar S. Tumor Angiogenesis and VEGFR-2: Mechanism, Pathways and Current Biological Therapeutic Interventions. Curr. Drug Metab. 2021;22(1):50–59. - PubMed
-
- Elkaeed E. B. Yousef R. G. Elkady H. Mehany A. B. Alsfouk B. A. Husein D. Z. Ibrahim I. M. Metwaly A. M. Eissa I. H. In silico, in vitro VEGFR-2 inhibition, and anticancer activity of a 3-(hydrazonomethyl) naphthalene-2-ol derivative. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023;41(16):7986–8001. - PubMed
-
- Taghour M. S. Elkady H. Eldehna W. M. El-Deeb N. Kenawy A. M. Abd El-Wahab A. E. Elkaeed E. B. Alsfouk B. A. Metwaly A. M. Eissa I. H. Discovery of new quinoline and isatine derivatives as potential VEGFR-2 inhibitors: design, synthesis, antiproliferative, docking and MD simulation studies. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023;41(21):11535–11550. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

