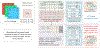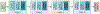Utilizing Pretrained Vision Transformers and Large Language Models for Epileptic Seizure Prediction
- PMID: 40337012
- PMCID: PMC12056660
- DOI: 10.1109/cdma61895.2025.00028
Utilizing Pretrained Vision Transformers and Large Language Models for Epileptic Seizure Prediction
Abstract
Repeated unprovoked seizures are a major source of concern for people with epilepsy. Predicting seizures before they occur is of interest to both machine-learning scientists as well as clinicians, and is an active area of research. The variability of EEG sensors, type of seizures, and specialized knowledge required for annotating the data complicates the large-scale annotation process essential for supervised predictive models. To address these challenges, we propose the use of Vision Transformers (ViTs) and Large Language Models (LLMs) that were originally trained on publicly available image or text data. Our work leverages these pre-trained models by refining the input, embedding, and classification layers in a minimalistic fashion to predict seizures. Our results demonstrate that LLMs outperforms the ViTs in patient-independent seizure prediction achieving a sensitivity of 79.02% which is 8% higher compared to ViTs and about 12% higher compared to a custom-designed ResNet-based model. Our work demonstrates the successful feasibility of pre-trained models for seizure prediction with its potential for improving the quality of life of people with epilepsy. Our code and related materials are available open-source at: https://github.com/pcdslab/UtilLLM_EPS/.
Keywords: Electroencephalography (EEG); Epilepsy; Large Language Model (LLM); Seizure Prediction; Vision Transformer (ViT).
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization, “Epilepsy,” 2023.
-
- Shoeb AH and Guttag J, “Application of Machine Learning To Epileptic Seizure Detection,” in ICML, pp. 975–982, jan 2010.
-
- Mohammad U and Saeed F, “MLSPred-Bench: ML-Ready Benchmark Leveraging Seizure Detection EEG data for Predictive Models,” bioRxiv preprint bioRxiv:2024.07.17.604006, pp. 1–13, 2024.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources