A glimpse into the application of the immunomodulatory effect of IL-2 in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 40337274
- PMCID: PMC12055818
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1552473
A glimpse into the application of the immunomodulatory effect of IL-2 in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
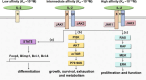
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a systemic autoimmune disease, which is mainly caused by the imbalance of immune cells. Current treatment regimens predominately rely on corticosteroids and immunosuppressive agents, accompanied by various side effects. Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is deemed an important cytokine for innate immune cells and adaptive immune cells, especially for the promotion of Treg cells. By combining IL-2/IL-2R system with engineered T cell-based immunotherapies to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of engineered T cells shows its potential in autoimmune diseases. But the pleiotropy of IL-2 may cause simultaneous stimulation and systemic toxicity, limiting its therapeutic use. There is a growing focus on using IL-2 in combination strategies for synergistic immune enhancement. In this article, we review the IL-2/IL-2R signaling, including IL-2 dependent signaling and IL-2 independent signaling, and discuss its functions in regulation of different immune cells. In addition, we summarize major clinical application of low-dose IL-2 treatment in SLE with or without other agents, such as rapamycin, tocilizumab and rituximab, present the IL-2 variants and fusion proteins designed for SLE, and highlight the future trends for research on these cytokine-based immunotherapies. It will help to design further optimized IL-2-based therapy for SLE.
Keywords: IL-2; SLE; engineered T cells; immunotherapy; interleukin-2.
Copyright © 2025 Xia and Qu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rosenberg S, Lotze M, Muul L, Leitman S, Chang A, Ettinghausen S, et al. Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med. (1985) 313:1485–92. 10.1056/NEJM198512053132327 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

