Analgesic Effectiveness of Ultrasound-Guided Unilateral Erector Spine Block Versus Paravertebral Block for Postoperative Management Among Adult Patients Undergoing Upper Abdominal Surgery: A Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 40337402
- PMCID: PMC12055060
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000003192
Analgesic Effectiveness of Ultrasound-Guided Unilateral Erector Spine Block Versus Paravertebral Block for Postoperative Management Among Adult Patients Undergoing Upper Abdominal Surgery: A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: The use of regional nerve blocks for postoperative analgesia in upper abdominal procedures is becoming more common. However, the postoperative analgesic effectiveness of each type of block remains controversial. This study aimed to compare the postoperative analgesic effect of ultrasound-guided erector spinae block versus paravertebral block (PVB) in upper abdominal surgery.
Methods: A hospital-based prospective cohort study was conducted on 78 adult patients undergoing upper abdominal surgery, including 39 in the erector spinae plane block (ESPB) and 39 in the PVB. The pain severity, time to first rescue analgesic administration, and total analgesic consumption were assessed 24 hour after surgery. The data were entered into Epi-Data version 4.6.02 and exported to SPSS version 26 for analysis.
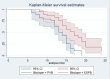
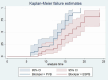
Result: In total, 78 patients were analyzed with no dropouts. Postoperative visual analog scores were lower in the ESPB group at 3rd, 6th, 12th, and 24th hours (P < 0.05). The ESPB group also had a significantly longer time to the first rescue analgesic requirement (mean time in hours, 16.8 [95% CI, 14.9-18.5]; P 0.03) than the PVB group (mean time in hours, 13.1 [95% CI, 11.9-14.3]; P 0.03). Furthermore, the ESPB group exhibited significantly lower opioid consumption at 24 hours postoperation than the PVB group in cases of upper abdominal surgery.
Conclusions: An ultrasound-guided unilateral ESPB for postoperative analgesia was more effective than a PVB for adult patients undergoing upper abdominal surgery. As a result, we recommend an ESPB over a PVB. The ESPB can serve as a valuable and safe alternative to either epidural or paravertebral nerve block for postoperative pain management.
Keywords: analgesia; erector spinae plane block; postoperative pain; upper abdominal surgery.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of ultrasound-guided intercostal nerve block, single-injection erector spinae plane block and multiple-injection paravertebral block on postoperative analgesia in thoracoscopic surgery: A randomized, double-blinded, clinical trial.J Clin Anesth. 2020 Feb;59:106-111. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2019.07.002. Epub 2019 Jul 19. J Clin Anesth. 2020. PMID: 31330457 Clinical Trial.
-
Postoperative analgesic effects of paravertebral block versus erector spinae plane block for thoracic and breast surgery: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 25;16(8):e0256611. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256611. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34432822 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of single-dose erector spinae plane block versus paravertebral block for pyeloplasty surgery in children - A prospective, randomized study.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Oct-Dec;40(4):686-692. doi: 10.4103/joacp.joacp_316_23. Epub 2024 Nov 15. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39759062 Free PMC article.
-
Analgesic effectiveness of preoperative ultrasound-guided erector spinae plane block versus paravertebral nerve block for breast surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis of four randomized controlled trials.Pain Pract. 2023 Jun;23(5):511-522. doi: 10.1111/papr.13208. Epub 2023 Feb 5. Pain Pract. 2023. PMID: 36695542
-
Comparative analysis of TPVB and ESPB for postoperative pain management in thoracic and breast surgeries.Future Sci OA. 2024 Dec;10(1):2430852. doi: 10.1080/20565623.2024.2430852. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Future Sci OA. 2024. PMID: 39578432 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abd-Elsayed A, Deer TR. Different types of pain. In: Abd-Elsayed A, ed. Pain. Cham:Springer; 2019: doi:10.1007/978-3-319-99124-5_3. - DOI
-
- Chin KJ, Malhas L, Perlas A. The erector spinae plane block provides visceral abdominal analgesia in bariatric surgery: a report of 3 cases. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2017;42:372–76. - PubMed
-
- Liheng L, Siyuan C, Zhen C, et al. . Erector spinae plane block versus transversus abdominis plane block for postoperative analgesia in abdominal surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Invest Surg 2022;35:1711–22. - PubMed
-
- Gomes Martins E, Frederico TN, Mansano A. Complications of thoracic procedures: paravertebral (PVT) blocks and erector spinae plane (ESP) block. Complications of Pain-Relieving Procedures: An Illustrated Guide 2022;2022:227–35.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
