Volatile oil of Acori tatarinowii rhizoma: potential candidate drugs for mitigating dementia
- PMID: 40337511
- PMCID: PMC12055781
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1552801
Volatile oil of Acori tatarinowii rhizoma: potential candidate drugs for mitigating dementia
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to elucidate the mitigating effects of the volatile oil of Acori tatarinowii rhizoma (ATR) on dementia, in order to provide a reference for future research and applications of the volatile oil of ATR in the field of dementia.
Materials and methods: A search strategy was developed using terms such as "Acori tatarinowii rhizoma," "Acorus tatarinowii Schott," "Asarone," and "Dementia." The literature search was conducted in PubMed, Web of Science, and Google Scholar, and studies not meeting the inclusion criteria were excluded. This study summarizes the main metabolites, active ingredients, toxicological properties, and pharmacokinetic characteristics of the volatile oil from ATR in mitigating dementia, with a particular focus on its potential mechanisms of action. Furthermore, the study highlights the limitations of existing research and offers insights into future research directions.
Results: The volatile oil of ATR mitigates dementia through multiple pathways, including reducing abnormal protein aggregation, promoting neurogenesis, inhibiting neuronal apoptosis, regulating neurotransmitters, improving synaptic function, modulating autophagy, countering cellular stress, reducing neuroinflammation, and alleviating vascular risk factors.
Conclusion: The multi-pathway pharmacological effects of the volatile oil of ATR are well-aligned with the complex mechanisms of dementia progression, highlighting its significant therapeutic potential for anti-dementia applications. This provides new perspectives for the development of more effective anti-dementia drugs. Nonetheless, further rigorous and high-quality preclinical and clinical investigations are required to address key issues, including the chemical characterization of the volatile oil of ATR, potential synergistic effects among active ingredients, toxicity profiles, and definitive clinical efficacy.
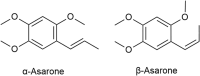
Keywords: Acori tatarinowii rhizoma; cognitive functions; dementia; α-asarone; β-asarone.
Copyright © 2025 Bu, Li, Ye, Wang, Song and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Asarone from Acori Tatarinowii Rhizoma Potentiates the Nerve Growth Factor-Induced Neuronal Differentiation in Cultured PC12 Cells: A Signaling Mediated by Protein Kinase A.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 29;11(9):e0163337. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163337. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27685847 Free PMC article.
-
[Research progress on pharmacological effects and mechanism of α-asarone and β-asarone in Acori Tatarinowii Rhizoma].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025 May;50(9):2305-2316. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20250211.602. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40461186 Review. Chinese.
-
Acori Tatarinowii Rhizoma: A comprehensive review of its chemical composition, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and toxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 16;14:1090526. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1090526. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37007031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Comparative Study on Quality of Volatile Oil of Acori Tatarinowii Rhizoma from Two Habitats].Zhong Yao Cai. 2015 Apr;38(4):770-3. Zhong Yao Cai. 2015. PMID: 26672346 Chinese.
-
Asarones from Acori Tatarinowii Rhizoma stimulate expression and secretion of neurotrophic factors in cultured astrocytes.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Aug 10;707:134308. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134308. Epub 2019 May 31. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 31153972
References
-
- Afshar S., Shahidi S., Rohani A. H., Soleimani Asl S., Komaki A. (2019). Protective effects of 5-HT(1A) receptor antagonist and 5-HT(2A) receptor agonist on the biochemical and histological features in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 96, 140–147. 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2019.01.008 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

