Osteocalcin and GPR158: linking bone and brain function
- PMID: 40337551
- PMCID: PMC12055796
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1564751
Osteocalcin and GPR158: linking bone and brain function
Abstract
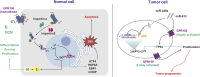
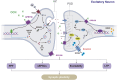
Osteocalcin (OCN), a small protein secreted by osteoblasts, has attracted significant attention for its role as an endocrine factor in regulating the central nervous system (CNS) via the bone-brain axis. As a critical receptor for OCN, G protein-coupled receptor 158 (GPR158) facilitates the proliferation, differentiation, and survival of neural cells while directly influencing neurons' structural and functional plasticity, thereby modulating cognitive function. Additionally, GPR158 is involved in cellular energy metabolism and interacts with proteins such as regulators of G protein signaling 7 (RGS7), broadening the understanding of OCN's impact on neural activity. Notably, GPR158 displays region- and cell type-specific bidirectional effects under certain pathological conditions, such as tumor development and mood regulation, adding complexity to its mechanisms of action. Although the precise biological mechanisms underlying the OCN/GPR158 signaling pathway remain incompletely understood, its association with neurodegenerative diseases (NDs), including Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD), is becoming increasingly evident. Thus, a systematic summary of OCN/GPR158 in CNS regulation and NDs will deepen understanding of its role in brain function and support the development of new therapeutic targets and strategies.
Keywords: GPR158; cellular activity; metabolism; neurodegenerative diseases; osteocalcin; synaptic plasticity.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Lou and Bian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pharmacological and resting state fMRI reveal Osteocalcin's effects on mouse brain regions with high Gpr37 and Gpr158 expression.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 24;15(1):10116. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95000-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40128223 Free PMC article.
-
Orphan Receptor GPR158 Is an Allosteric Modulator of RGS7 Catalytic Activity with an Essential Role in Dictating Its Expression and Localization in the Brain.J Biol Chem. 2015 May 29;290(22):13622-39. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.645374. Epub 2015 Mar 19. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25792749 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging roles of GPR158 in the regulation of the endocrine system.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Nov 18;10:1034348. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1034348. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36467406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RbAp48 Protein Is a Critical Component of GPR158/OCN Signaling and Ameliorates Age-Related Memory Loss.Cell Rep. 2018 Oct 23;25(4):959-973.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.09.077. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30355501 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction, mechanism and function of GPR158-RGS7 cross-talk.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2022;193(1):167-176. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2022.06.007. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 36357076 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

