Renoprotective Action of Linagliptin Among Diabetic Kidney Disease Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40337567
- PMCID: PMC12057586
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.81833
Renoprotective Action of Linagliptin Among Diabetic Kidney Disease Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Despite pharmacological and lifestyle changes, hyperglycemia management in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients, combined with a risk for cardio-renal problems, continues to present a significant challenge for doctors. Linagliptin has been found to have a renoprotective effect in diabetic nephropathy patients in recent studies. This systematic review and meta-analysis (SRMA) was conducted to synthesize available information so as to better understand if linagliptin has a renoprotective effect in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with nephropathy. Three databases were searched from January 2013 to December 2022 to identify all published studies reporting "linagliptin's effect in patients with diabetic nephropathy". Owing to the heterogeneity of the included studies, the authors have employed a random-effects model to examine the data in this meta-analysis. Standardized mean differences (SMD) for continuous outcomes were used to compute effect sizes. The final analysis included five studies. The change in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) did not show a statistically significant difference between the group on linagliptin and the other group on placebo, at baseline (mean difference = 1.19, p = 0.28), after three months of intervention in the selected three studies (mean difference = 0.51, p = 0.85), and after six months of intervention in the selected two studies (mean difference = 0.72, p = 0.70). The study found that linagliptin did not have a significant renoprotective effect in patients with type 2 diabetes, indicating no substantial benefit in slowing kidney disease progression. For diabetes patients with chronic renal disease, linagliptin may be a helpful renoprotective treatment choice, but in the future, more robust and longer-duration research is warranted to establish the inference.
Keywords: diabetes; dipeptidyl peptidase-4; dpp-4; linagliptin; nephropathy; renoprotective.
Copyright © 2025, Panda et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


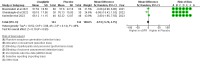


References
-
- People with diabetes, in 1,000s. [ Jun; 2024 ]. 2024. https://diabetesatlas.org/data-by-indicator/diabetes-estimates-20-79-y/p... https://diabetesatlas.org/data-by-indicator/diabetes-estimates-20-79-y/p...
-
- Long-term risks of kidney living donation: review and position paper by the ERA-EDTA DESCARTES working group. Maggiore U, Budde K, Heemann U, et al. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017;32:216–223. - PubMed
-
- Death, end-stage renal disease and renal function decline in patients with diabetic nephropathy in French cohorts of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Hadjadj S, Cariou B, Fumeron F, et al. Diabetologia. 2016;59:208–216. - PubMed
-
- Powers AC, Stafford JM, Rickels MR. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 21st Edition. United States: McGraw-Hill Education; 2022. Diabetes mellitus: complications.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
