Carbamazepine-Induced Oral Lichenoid Reaction: A Report of a Rare Case
- PMID: 40337574
- PMCID: PMC12057648
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.81835
Carbamazepine-Induced Oral Lichenoid Reaction: A Report of a Rare Case
Abstract
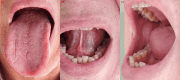
Lichenoid drug reactions (LDRs) are rare adverse effects that resemble lichen planus both clinically and histopathologically. Although cutaneous involvement is more common, oral manifestations are relatively uncommon. Carbamazepine, a widely used antiepileptic drug, has been associated with various cutaneous adverse reactions, but oral lichenoid reactions (OLRs) due to carbamazepine are rarely reported. In this case report, we present a 62-year-old male patient who developed painful white reticular plaques on the buccal mucosa and lateral borders of the tongue after using carbamazepine for approximately 14 months. The lesions completely regressed within three weeks following the discontinuation of the drug. No dental restorations or other possible local irritants were detected. Although histopathological confirmation could not be obtained due to the patient's refusal of a biopsy, the clinical appearance and full remission after drug cessation strongly supported the diagnosis. This case highlights the importance of considering drug-induced OLRs in the differential diagnosis of oral mucosal lesions, especially in patients using medications known to cause lichenoid eruptions. Early recognition and discontinuation of the offending drug are crucial for resolution and patient comfort.
Keywords: adverse drug reaction; buccal mucosa; carbamazepine; drug-induced lesions; oral lichenoid reaction.
Copyright © 2025, Cinar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Lichenoid drug reactions [Article in German] Merk HF, Vanstreels L, Megahed M. Hautarzt. 2018;69:116–120. - PubMed
-
- Cutaneous lichenoid drug eruptions: a narrative review evaluating demographics, clinical features and culprit medications. Maul JT, Guillet C, Oschmann A, et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:965–975. - PubMed
-
- Lichenoid drug eruptions. Halevy S, Shai A. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;1:249–255. - PubMed
-
- Skin reactions to carbamazepine. Roberts DL, Marks R. Arch Dermatol. 1981;117:273–275. - PubMed
-
- Lichenoid reaction to carbamazepine in the oral mucosa: case report. Artico G, Bruno IS, Seo J, Hirota SK, Acay R, Migliari DA. An Bras Dermatol. 2011;86:0–5. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
