Massive Scrotal Lymphedema in an Adolescent with Intellectual Disability: A Rare Case of Infection-Related Scrotal Enlargement Requiring Subtotal Scrotectomy
- PMID: 40337589
- PMCID: PMC12056880
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.81821
Massive Scrotal Lymphedema in an Adolescent with Intellectual Disability: A Rare Case of Infection-Related Scrotal Enlargement Requiring Subtotal Scrotectomy
Abstract
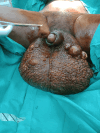
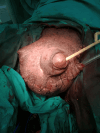
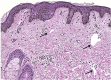
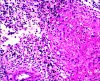
An uncommon disorder marked by aberrant fluid accumulation brought on by lymphatic blockage, scrotal lymphedema presents major functional, cosmetic, and hygiene problems. It can be acquired or congenital; the most often occurring causes are infection, persistent inflammation, and filariasis. This case report describes a 17-year-old male patient with intellectual disability who had severe scrotal lymphedema that gradually developed over four years, causing problems with ambulation and hygienic care. Under a clinical examination, the scrotum (40 x 15 cm) was swollen and expanded, hiding the penis but having palpable testes. Ultrasound verified without testicular involvement scrotal wall thickening. After a subtotal scrotectomy preserves the testes, penis, and spermatic cord, scrotal reconstruction was done considering the functional limitation. Chronic inflammatory alterations without filarial organisms revealed by histopathology suggested an etiology connected to infections. The patient healed postoperatively with better mobility and hygienic standards. This example emphasizes the need for early identification and surgical intervention in controlling large scrotal lymphedema to maximize functional and cosmetic results.
Keywords: chronic inflammation; hypertrophy; infection-related lymphedema; reconstruction; scrotal lymphedema.
Copyright © 2025, Saqlain et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Giant scrotal elephantiasis of inflammatory etiology: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2007 Jun 2;1:23. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-1-23. J Med Case Rep. 2007. PMID: 17543128 Free PMC article.
-
'Hanger‑shaped' scrotectomy: A novel technique for the management of penoscrotal lymphedema: A case report.Med Int (Lond). 2022 Oct 20;2(6):33. doi: 10.3892/mi.2022.58. eCollection 2022 Nov-Dec. Med Int (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36699154 Free PMC article.
-
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising From Massive Localized Lymphedema of Scrotum Mimicking Scrotal Smooth Muscle Hamartoma of Dartos: A Case Report.Am J Dermatopathol. 2015 Jul;37(7):551-4. doi: 10.1097/DAD.0000000000000135. Am J Dermatopathol. 2015. PMID: 26091513
-
Penile and scrotal lymphedema associated with hidradenitis suppurativa: Case report and review of surgical options.Cir Cir. 2019;86(1):77-80. doi: 10.24875/CIRUE.M18000012. Cir Cir. 2019. PMID: 30951036 Review. English.
-
[Penile and scrotal lymphedema associated with hidradenitis suppurativa: Case report and review of surgical options].Cir Cir. 2018;86(1):84-88. doi: 10.24875/CIRU.M18000007. Cir Cir. 2018. PMID: 29681638 Review. Spanish.
References
-
- Scrotal lymphedema and its conservative treatment: a rare complication of circumcision. Akan S, Urkmez B, Artuk I, Urkmez A. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2020;30:94–95. - PubMed
-
- Urogenital tuberculosis - epidemiology, pathogenesis and clinical features. Muneer A, Macrae B, Krishnamoorthy S, Zumla A. Nat Rev Urol. 2019;16:573–598. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
