Design of ELISA-based diagnostic system for detection of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli
- PMID: 40337686
- PMCID: PMC12053411
- DOI: 10.18502/ijm.v17i2.18388
Design of ELISA-based diagnostic system for detection of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli
Abstract
Background and objectives: Escherichia coli (E. coli) O157:H7 is an intestinal pathogen of humans and animals, which causes serious gastrointestinal, urinary tract infection and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Connecting to the host cell is important in pathogenesis. EspA, Intimin and Tir proteins (EIT) are the most important bacterial features in the process of binding. These antigens can be very useful in detecting these bacteria. The aim of this study was to produce recombinant EspA, Intimin and Tir proteins (rEIT) to detect pathogenic E. coli O157:H7 by means of ELISA method.
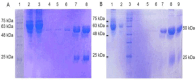
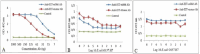
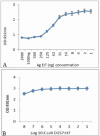
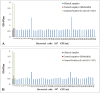
Materials and methods: The eit recombinant gene was expressed using IPTG in E. coli BL21 (DE3) and evaluated by western blotting. The purified rEIT protein was injected to rabbits and mice subcutaneously. Purified antibody was evaluated using indirect, competitive and sandwich ELISA confirming the precise detection of E. coli O157: H7.
Results: Indirect, competitive and sandwich ELISA specifically detected E. coli O157:H7 and each methods had the ability to identify more than 104, 104, 103 bacteria. The specificity of this method was evaluated by Entroheamoragic E. coli, enterotoxygenic E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Vibrio cholera and Acinetobacter.
Conclusion: These methods are the fastest, most accurate and cost effective methods for diagnosis of E. coli O157: H7, comparing to the conventional methods.
Keywords: Competitive ELISA; Escherichia coli O157:H7; Indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA); Sandwich ELISA.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cutting-Edge Exploration of a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Coupled Electrochemiluminescence Mechanism Based on Organic Cation Side-Chain Construction for the Identification and Detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7.ACS Sens. 2025 Jun 27;10(6):4105-4115. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.5c00172. Epub 2025 May 15. ACS Sens. 2025. PMID: 40375657
-
Systematic review: are antibiotics detrimental or beneficial for the treatment of patients with Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection?Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Sep 1;24(5):731-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.03036.x. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16918877
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Smoking cessation medicines and e-cigarettes: a systematic review, network meta-analysis and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2021 Oct;25(59):1-224. doi: 10.3310/hta25590. Health Technol Assess. 2021. PMID: 34668482
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
-
- Velusamy V, Arshak K, Korostynska O, Oliwa K, Adley C. An overview of foodborne pathogen detection: In the perspective of biosensors. Biotechnol Adv 2010; 28: 232–254. - PubMed
-
- Abadias M, Usall J, Anguera M, Solsona C, Viñas I. Microbiological quality of fresh, minimally-processed fruit and vegetables, and sprouts from retail establishments. Int J Food Microbiol 2008; 123: 121–129. - PubMed
-
- Wu C-J, Hsueh P-R, Ko W-C. A new health threat in Europe: Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli O104: H4 infections. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 2011; 44: 390–393. - PubMed
-
- Yazdanparast A, Mousavi SL, Rasooli I, Amani J, Jalalinadoushan M. Immunogenical study of chimeric recombinant intimin-Tir of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in mice. Arch Clin Infect Dis 2012; 7: 45–51.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
