Insights into global transcriptomic profile of biofilm producing Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates from chronic foot ulcers
- PMID: 40337687
- PMCID: PMC12053402
- DOI: 10.18502/ijm.v17i2.18394
Insights into global transcriptomic profile of biofilm producing Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates from chronic foot ulcers
Abstract
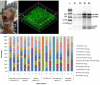
Background and objectives: Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is one of the predominant biofilm producing pathogen in leprosy foot ulcer (LFU). The objective of this study was to identify the transcriptome profile through Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) approach in mature biofilm of leprosy foot ulcer isolate of S. aureus.
Materials and methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted from July 2019 to May 2022 and a total of twenty-seven S. aureus isolates were collected from the foot ulcers of leprosy patients. All S. aureus isolates were screened for biofilm formation in vitro. Initially, two potential biofilm producing isolates and two planktonic cells were selected for transcriptome comparison.
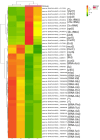
Results: With reference to transcriptome profile, out of 2,842 genes, 2,688 genes in mature biofilm and 2,685 genes in planktonic cells were expressed. Among them, forty-five differentially expressed genes with 32 and 13 genes showing up and down regulation respectively were obtained.
Conclusion: The research emphasizes the need for continued exploration into the mechanisms of biofilm formation by S. aureus, particularly in the context of leprosy foot ulcers. Understanding these pathways not only aids in grasping the complexity of chronic infections but also paves the way for innovative therapeutic approaches aimed at mitigating biofilm-related complications in clinical settings.
Keywords: Biofilm; Confocal microscopy; Leprosy foot ulcer; Staphylococcus aureus; Transcriptome.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of icaA and icaD Genes Involved in Biofilm Formation in Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Clinical Sources Using Reverse Transcriptase PCR.Arch Razi Inst. 2024 Dec 31;79(6):1329-1335. doi: 10.32592/ARI.2024.79.6.1329. eCollection 2024 Dec. Arch Razi Inst. 2024. PMID: 40599458 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic and genotypic characteristics of mecA - positive oxacillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus isolated from patients with bloodstream infection in a tertiary hospital in Southern Brazil.Braz J Microbiol. 2024 Sep;55(3):2705-2713. doi: 10.1007/s42770-024-01420-z. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Braz J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38896343 Free PMC article.
-
Topical antimicrobial agents for treating foot ulcers in people with diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 14;6(6):CD011038. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011038.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28613416 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for the eradication of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in people with cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 21;7(7):CD009650. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009650.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Dec 13;12:CD009650. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009650.pub5. PMID: 30030966 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Interventions for the eradication of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in people with cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Dec 13;12(12):CD009650. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009650.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36511181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sehgal VN, Prasad PV, Kaviarasan PK, Rajan D. Trophic skin ulceration in leprosy: evaluation of the efficacy of topical phenytoin sodium zinc oxide paste. Int J Dermatol 2014; 53: 873–878. - PubMed
-
- Gibbs NK, Ochalek J, Napit IB, Shrestha D, Goncalves PS, Lilford RJ, et al. Health-related quality of life implications of plantar ulcers resulting from neuropathic damage caused by leprosy: An analysis from the trial of autologous blood products (TABLE trial) in Nepal. PloS One 2025; 20(2): e0315944. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
