Activity of cefiderocol on extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa from burn wound infections in Mansoura, Egypt
- PMID: 40337703
- PMCID: PMC12053395
- DOI: 10.18502/ijm.v17i2.18384
Activity of cefiderocol on extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa from burn wound infections in Mansoura, Egypt
Abstract
Background and objectives: Increased Pseudomonas aeruginosa antibiotic resistance limits treatment options and is associated with a higher level of mortality and mordacity. The purpose of this research was to identify class 1 and 2 integrons, carbapenemase, SHV, and TEM genes in extensively drug-resistant (XDR) P. aeruginosa isolated from infected burns and evaluate their in vitro cefiderocol activity.
Materials and methods: By using the disc diffusion method, the antimicrobial susceptibility of 110 P. aeruginosa isolates collected from infected burns were evaluated. XDR P. aeruginosa were screened phenotypically for carbapenemase and extended spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) production. Both MIC Test Strip and disc diffusion were employed to test the cefiderocol susceptibility. PCR was used to assess carbapenemase, SHV and TEM genes and integrons class 1 and 2.
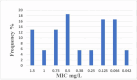
Results: From the 110 P. aeruginosa, 54 isolates (49%) were XDR. TEM gene was detected in 35 isolates. Among XDR isolates, carbapenemase genes were detected in 31.5%, with NDM being predominant Thirty XDR isolates had class1 integrons. All isolates were sensitive to cefiderocol and its MIC50/MIC90 was 0.5/1.5mg/L (range 0.064-1.5mg/L).
Conclusion: Nearly half the P. aeruginosa isolates from burn infections were extensively drug-resistant. Cefiderocol's in vitro activity demonstrated that it is a promising therapy alternative for treating extensively drug-resistant P. aeruginosa in burn patients.
Keywords: Burn; Carbapenemase; Extended detection and response; NDM; Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular and genomic insights into multidrug-resistant (MDR) and extensively drug-resistant (XDR) Pseudomonas aeruginosa causing burn wound infections in Bangladesh.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 15;15(1):25445. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11614-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40659765 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its coexistence with β-lactamases at a tertiary care hospital in a low-resource setting: a cross-sectional study with an association of risk factors.Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2025 Jun 18;12:20499361251345920. doi: 10.1177/20499361251345920. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40538920 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of metallo-beta-lactamase producers among carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa from clinical samples in a tertiary care hospital, Lucknow, India.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Aug;398(8):10273-10284. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03913-6. Epub 2025 Feb 18. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39964472
-
Antibiotic strategies for eradicating Pseudomonas aeruginosa in people with cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 25;4(4):CD004197. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004197.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jun 2;6:CD004197. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004197.pub6. PMID: 28440853 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Antiseptics for burns.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 12;7(7):CD011821. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011821.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28700086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aljanaby AAJ, Aljanaby IAJ. Prevalence of aerobic pathogenic bacteria isolated from patients with burn infection and their antimicrobial susceptibility patterns in Al-Najaf City, Iraq- a three-year cross-sectional study. F1000Res 2018; 7: 1157.
-
- Oliver A, Rojo-Molinero E, Arca-Suarez J, Beşli Y, Bogaerts P, Cantón R, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa antimicrobial susceptibility profiles, resistance mechanisms and international clonal lineages: update from ESGARS-ESCMID/ISARPAE Group. Clin Microbiol Infect 2024; 30: 469–480. - PubMed
-
- Ghasemian S, Karami-Zarandi M, Heidari H, Khoshnood S, Kouhsari E, Ghafourian S, et al. Molecular characterizations of antibiotic resistance, biofilm formation, and virulence determinants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from burn wound infection. J Clin Lab Anal 2023; 37(4): e24850. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources