Dynamic Associations among Caregiver Romantic Satisfaction, Depressive Symptoms, and School-aged Child Problem Behavior
- PMID: 40337757
- PMCID: PMC12058217
- DOI: 10.1007/s10826-023-02599-9
Dynamic Associations among Caregiver Romantic Satisfaction, Depressive Symptoms, and School-aged Child Problem Behavior
Abstract
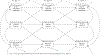
Parental mental health and social relationships are related to children's problem behaviors in a complex way, but the intricate nuances of such effects remain understudied. Within the context of a prospectively followed, randomized controlled trial of a parenting intervention (the Family Check-Up), the current study investigated reciprocal relations among primary caregiver romantic satisfaction, depressive symptoms and children's externalizing behaviors during the school-age period using a sample of low-income families from diverse racial/ethnic backgrounds. Primary caregiver self-reported romantic satisfaction and depressive symptoms, and caregiver- and teacher-reported child externalizing behavior problems were measured at child ages 7.5, 8.5, and 9.5. To prevent against bias for the inclusion of couples in longer- versus shorter-term relationships in the literature, primary caregivers with different romantic partners across waves of the study were included. Leveraging complex modeling to more thoroughly understand dynamic associations among interparental romantic satisfaction, depressive symptoms, and child problem behavior, nested model comparisons among five models were conducted to assess which model best fit the data in the control and intervention groups separately. For the control group, within a looped, clockwise paths model, child externalizing behaviors positively predicted caregiver depressive symptoms one year later, and caregiver depressive symptoms predicted lower levels of caregiver romantic satisfaction one year later. However, for the intervention group, child externalizing behavior was not related to caregiver depressive symptoms nor to romantic satisfaction across waves. The findings highlight many avenues for prevention and intervention to support positive family processes.
Keywords: externalizing problem behavior; family process; looped panel structural equation model; low-income families; school-aged children.
Figures
References
-
- Achenbach TM (1991). Manual for the Teacher’s Report Form and 1991 Profile. Burlington: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
-
- Amato PR (2010). Research on divorce: Continuing trends and new developments. Journal of Marriage and Family, 72(3), 650–666. 10.1111/j.1741-3737.2010.00723.x - DOI
-
- Amato PR & Fowler F. (2002). Parenting practices, child adjustment, and family diversity. Journal of Marriage and Family, 64, 703–716. 10.1111/j.1741-3737.2002.00703.x - DOI
-
- Beach SR, Katz J, Kim S, & Brody GH (2003). Prospective effects of marital satisfaction on depressive symptoms in established marriages: A dyadic model. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 20(3), 355–371. 10.1177/0265407503020003005 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources