Supraspinal kappa-opioid receptors: new therapeutic strategies for pain, pruritus, and negative emotions
- PMID: 40338314
- PMCID: PMC12062100
- DOI: 10.1007/s00221-025-07066-z
Supraspinal kappa-opioid receptors: new therapeutic strategies for pain, pruritus, and negative emotions
Abstract
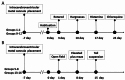
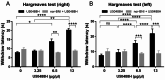
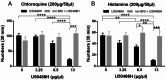
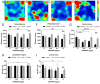
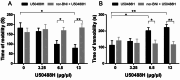
Research on kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) regulation of pain and itching has focused primarily on spinal and peripheral levels. However, the role of central KOR in this process, as well as the mechanisms exacerbating negative emotional responses to pain and itching, remains unknown. Therefore, this study aimed to utilize the advantages of intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) administration of U50488H to explore supraspinal KOR activation on pain, itching, and negative emotions. U50488H, a prototypical KOR agonist, was administered i.c.v., with physiological saline as the control. The Hargreaves test and intradermal injection of histamine and chloroquine were conducted to assess thermal pain and itch behavior, respectively. The elevated plus maze (EPM), open field test (OFT), and tail suspension test (TST) were performed to evaluate negative emotions. i.c.v. administration of U50488H increased thermal pain latencies, reduced scratching behavior, and decreased locomotor activity in the central zone of the OFT and in the open arms of the EPM, while increasing immobility in the TST. i.c.v. pretreatment with the KOR antagonist nor-Binaltorphimine dihydrochloride reversed all of the above behaviors. In conclusion, central administration of U50488H can exhibit analgesic and antipruritic effects while also inducing negative emotional responses. Our results highlight the potential of supraspinal KOR as a promising therapeutic target in the combined treatment of pain, pruritus, and negative emotions.
Keywords: Anxiety; Depression; Itch; Kappa-opioid receptor; Pain; U50488H.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Aldrich JV, McLaughlin JP (2021) Peptide kappa opioid receptor ligands and their potential for drug development. In: Liu-Chen L-Y, Inan S (eds) The kappa opioid receptor. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 197–220. 10.1007/164_2021_519
-
- Andoh T, Suzuki K, Konno M, Tsuneyama K, Kuraishi Y (2020) Pharmacological characterization of a novel mouse model of cholestatic pruritus. Biol Pharm Bull 43:1111–1117. 10.1248/bpb.b20-00097 - PubMed
-
- Brust TF, Morgenweck J, Kim SA, Rose JH, Locke JL, Schmid CL, Zhou L, Stahl EL, Cameron MD, Scarry SM, Aubé J, Jones SR, Martin TJ, Bohn LM (2016) Biased agonists of the kappa opioid receptor suppress pain and itch without causing sedation or dysphoria. Sci Signal 9:117. 10.1126/scisignal.aai8441 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cahill C, Tejeda HA, Spetea M, Chen C, Liu-Chen L-Y (2021) Fundamentals of the dynorphins/kappa opioid receptor system: from distribution to signaling and function. In: Liu-Chen L-Y, Inan S (eds) The kappa opioid receptor. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 3–21. 10.1007/164_2021_433
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ZR2020MH131/Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- 2019WS316/Project of Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Plan of Shandong Province
- 202001020608/Project of Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Plan of Shandong Province
- 2023NSFSC1566/Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

