The role of nanomedicine and artificial intelligence in cancer health care: individual applications and emerging integrations-a narrative review
- PMID: 40338421
- PMCID: PMC12061837
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-02469-4
The role of nanomedicine and artificial intelligence in cancer health care: individual applications and emerging integrations-a narrative review
Abstract
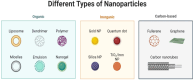
Cancer remains one of the deadliest diseases globally, significantly impacting patients' quality of life. Addressing the rising incidence of cancer deaths necessitates innovative approaches such as nanomedicine and artificial intelligence (AI). The convergence of nanomedicine and AI represents a transformative frontier in cancer healthcare, promising unprecedented advancements in diagnosis, treatment, and patient management. This narrative review explores the distinct applications of nanomedicine and AI in oncology, alongside their synergistic potential. Nanomedicine leverages nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery, enhancing therapeutic efficacy while minimizing adverse effects. Concurrently, AI algorithms facilitate early cancer detection, personalized treatment planning, and predictive analytics, thereby optimizing clinical outcomes. Emerging integrations of these technologies could transform cancer care by facilitating precise, personalized, and adaptive treatment strategies. This review synthesizes current research, highlights innovative individual applications, and discusses the emerging integrations of nanomedicine and AI in oncology. The goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of how these cutting-edge technologies can collaboratively improve cancer diagnosis, treatment, and patient prognosis.
Keywords: AI in healthcare; Artificial intelligence; Cancer; Digital healthcare; Drug delivery; Nanomedicine; Nanoparticles; Oncology.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. I hereby declare that this submission is entirely my own work, in my own words, and that all sources used in researching it are fully acknowledged and all quotations properly identified. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All the authors have read and agreed to the final copy of the finding as contained in the manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
