Small interfering RNA effect on lipoprotein(a): a systematic review
- PMID: 40338464
- PMCID: PMC12062474
- DOI: 10.1186/s43044-025-00635-1
Small interfering RNA effect on lipoprotein(a): a systematic review
Abstract
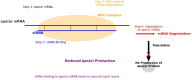
Background: This systematic review investigates the effect of small interfering RNA (siRNA) therapies on lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] levels. The purpose is to evaluate the outcomes of recent randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving siRNA treatments aimed at lowering Lp(a) levels, a known cardiovascular risk factor.
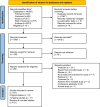
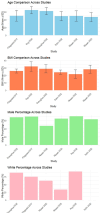
Methods: A comprehensive search across multiple databases was conducted, identifying 20 published and ongoing RCTs that examined the effects of siRNA therapies such as inclisiran, olpasiran, and SLN360 on Lp(a) levels. The included studies were analyzed to assess Lp(a) reductions and other lipid-related outcomes.
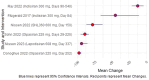
Results: The RCTs demonstrated significant reductions in Lp(a) levels following siRNA therapy. Additional reductions were noted in LDL-c and apolipoprotein B levels. Side effects were typically mild, including injection site reactions.
Conclusions: siRNA therapies show promise in effectively lowering Lp(a) levels, with minimal adverse effects. However, further research is required to establish their long-term safety and efficacy.
Keywords: Apolipoprotein B; Cardiovascular risk; Coronary artery disease; Hyperlipidemia; Inclisiran; LDL-c; Lipid-lowering therapy; Lipoprotein(a); Lp(a); Olpasiran; Randomized controlled trials; SLN360; siRNA.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Silverman MG, Ference BA, Im K et al (2016) Association between lowering LDL-C and cardiovascular risk reduction among different therapeutic interventions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 316(12):1289–1297. 10.1001/jama.2016.13985 - PubMed
-
- Force M. 2019 esc/eas guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. 2019. https://boris.unibe.ch/1493.
-
- Tasdighi E, Adhikari R, Almaadawy O, Leucker TM, Blaha MJ (2023) LP(a): structure, genetics, associated cardiovascular risk, and emerging therapeutics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-031023-100609 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
