Thrombospondin-1 inhibits alternative complement pathway activation in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis
- PMID: 40338657
- PMCID: PMC12208556
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI180062
Thrombospondin-1 inhibits alternative complement pathway activation in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis
Abstract
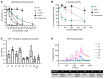
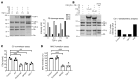
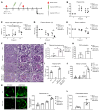
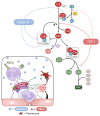
Complement activation is a relevant driver in the pathomechanisms of vasculitis. The involved proteins in the interaction between endothelia, complement, and platelets in these conditions are only partially understood. Thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1), found in platelet α-granules and released from activated endothelial cells, interacts with factor H (FH) and vWF. However, to our knowledge, direct regulatory interaction with the complement cascade has not yet been described. Our study shows that TSP-1 is a potent, FH-independent inhibitor of the alternative complement pathway. TSP-1 binds to complement proteins and inhibits cleavage of C3 and C5 and the formation of the membrane attack complex. We validated complement-regulatory function in blood samples from patients with primary complement defects. The physiological relevance of TSP-1 was demonstrated in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis (AAV) by significantly enhanced TSP-1 staining in glomerular lesions and increased complement activity and NETosis after TSP-1 deficiency in an in vitro and in vivo model of AAV. The complement-inhibiting function of TSP-1 represents an important mechanism in the interaction of endothelia and complement. In particular, the interplay between released TSP-1 and the complement system locally, especially on surfaces, influences the balance between complement activation and inhibition and may be relevant in various vascular diseases.
Keywords: Complement; Endothelial cells; Immunology; Inflammation; Vascular biology; Vasculitis.
Figures





References
-
- Dubernard V, et al. Evidence for an alpha-granular pool of the cytoskeletal protein alpha-actinin in human platelets that redistributes with the adhesive glycoprotein thrombospondin-1 during the exocytotic process. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997;17(10):2293–2305. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.17.10.2293. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

