Development and evaluation of immunogenicity and protective efficacy of two recombinant attenuated newcastle disease viruses expressing the VP2 protein of infectious bursal disease virus
- PMID: 40339237
- PMCID: PMC12138426
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105253
Development and evaluation of immunogenicity and protective efficacy of two recombinant attenuated newcastle disease viruses expressing the VP2 protein of infectious bursal disease virus
Abstract
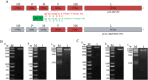
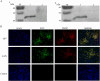
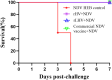
Newcastle disease (ND) and Infectious bursal disease (IBD) are highly contagious and economically significant viral diseases affecting poultry worldwide. Despite widespread vaccination, current vaccines often require multiple doses and provide limited protection against emerging strains. This study developed and evaluated bivalent vaccines based on recombinant Newcastle disease virus (NDV) expressing the VP2 protein of a novel variant Infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV), SHG19 strain. To enhance immunogenicity and antigenic compatibility, two recombinant NDVs were generated: rHV, using a modified genotype VII HEB strain backbone, and rLHV, using the lentogenic LaSota backbone incorporating HEB F and HN genes. Protective efficacy was evaluated in specific pathogen-free (SPF) chickens through immunization followed by challenges with both NDV and IBDV. Results demonstrated robust humoral immune responses, significant reductions in viral shedding, and effective dual protection against both pathogens. These findings highlight the potential of NDV-based bivalent vaccines to streamline vaccination protocols and offer enhanced protection against circulating NDV and IBDV strains.
Keywords: Infectious bursal disease virus; Newcastle disease virus; VP2 protein; immunogenicity; recombinant attenuated virus.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Charkhkar S., Bashizade M., Sotoudehnejad M., Ghodrati M., Bulbuli F., Akbarein H. The evaluation and importance of Newcastle disease’s economic loss in commercial layer poultry. J. Poult. Sci. Avian Dis. 2024;2:1–4. doi: 10.61838/kman.jpsad.2.1.1. - DOI
-
- Courtillon C., Allée C., Amelot M., Keita A., Bougeard S., Härtle S., Rouby J.-C., Eterradossi N., Soubies S.M. Blood B cell depletion reflects immunosuppression induced by live-attenuated infectious bursal disease vaccines. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022;9 doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.871549. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dewidar A.A.A., Kilany W.H., El-Sawah A.A., Shany S.A.S., Dahshan A.-H.M., Hisham I., Elkady M.F., Ali A. Genotype VII.1.1-based Newcastle disease virus vaccines afford better protection against field isolates in commercial broiler chickens. Animals. 2022;12:1696. doi: 10.3390/ani12131696. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

