Does the coronal plane alignment of the ankle and subtalar joints normalize after total knee arthroplasty?
- PMID: 40340766
- PMCID: PMC12063276
- DOI: 10.1186/s43019-025-00272-7
Does the coronal plane alignment of the ankle and subtalar joints normalize after total knee arthroplasty?
Abstract
Background: Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) alters the lower extremity alignment, potentially affecting adjacent joints such as the ankle and subtalar joints. However, the relationship between changes in hindfoot alignment and ankle osteoarthritis (OA) after TKA remains incompletely understood. The purpose of this study was to clarify whether ankle and subtalar alignment normalizes after TKA and to identify factors associated with persistent malalignment.
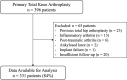
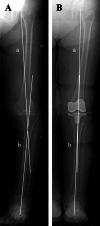
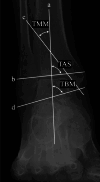
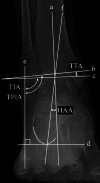
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 331 patients who underwent unilateral mechanical alignment (MA) TKA for knee osteoarthritis. A control group of 40 healthy subjects was used to define normal alignment ranges. Whole-leg anteroposterior weight-bearing radiographs were obtained preoperatively and 2 months postoperatively. Alignment parameters included the hip-knee-ankle angle (HKA), tibiotalar tilt angle (TTA), tibial plafond inclination angle (TPIA), talar inclination angle (TIA), and hindfoot alignment angle (HAA). Pre- and postoperative values were compared using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, and changes in the proportion of patients within the normal range were determined. Wilcoxon rank-sum tests and chi-squared tests were used for group comparisons, and multivariate logistic regression identified independent predictors of persistent malalignment.
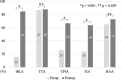
Results: HKA improved after TKA (-12° to -2.0°), with corresponding improvements in TPIA (99° to 94°) and TIA (99° to 95°) (all p < 0.001), indicating a significant correction toward neutral alignment. The proportion of patients within normal range increased postoperatively from 16% to 85% for HKA, 26% to 67% for TPIA, 24% to 64% for TIA, and 65% to 73% for HAA. Multivariate analysis identified ankle OA (odds ratio [OR] = 6.62 for TTA), female sex (OR = 2.32 for TPIA; OR = 3.19 for TIA), and varus knee alignment (OR = 2.81 for TIA) as independent predictors of persistent malalignment.
Conclusions: MA-TKA facilitates partial normalization of coronal hindfoot alignment, particularly at the tibial plafond and talus. However, female sex, varus knee deformity, and pre-existing ankle OA independently limit full correction. These findings highlight the biomechanical interdependence between the knee and hindfoot and may guide surgical decision-making and patient-specific alignment strategies.
Keywords: Ankle osteoarthritis; Coronal alignment; Hindfoot alignment; Subtalar joint; Total knee arthroplasty.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Each author certifies that his/her institution approved the human subject protocol for this investigation and that all investigations were conducted in conformity with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration. Ethical approval for this study was obtained from the institutional ethical review board of the Faculty of Medicine, Saga University (no. 2022-06-R-05), and the requirement for informed consent of the participants was waived by the institutional ethical review board of the Faculty of Medicine, Saga University, owing to the retrospective nature of the study. Consent for publication: Ethical approval for this study was obtained from the Faculty of Medicine, Saga University (no. 2022-06-R05). Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

