Transcriptome analysis and genome-wide identification of WRKY gene family in Leonurus japonicus under drought stress
- PMID: 40340820
- PMCID: PMC12063297
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-025-06606-7
Transcriptome analysis and genome-wide identification of WRKY gene family in Leonurus japonicus under drought stress
Abstract
Background: Leonurus japonicus (L. japonicus) is a herbaceous flowering plant, widely distributed in Asia. Drought is one of the primary environmental stress factors affecting L. japonicus growth. Previous studies have demonstrated that WRKY transcription factors (TFs) play a crucial role in plant responses to drought stress. So far, there has been no research on the function of WRKY genes in L. japonicus.
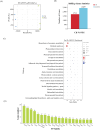
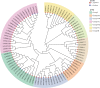
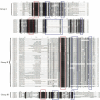
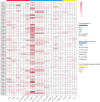
Results: The physiological experiment results showed that drought stress significantly increased the malondialdehyde (MDA), proline, and hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) content of L. japonicus. Transcriptome analysis revealed significant changes in the expression levels of the WRKY gene family. Based on bioinformatics analysis, 67 WRKY genes (LjWRKYs) were identified in the genome of L. japonicus, with amino acid lengths ranging from 85 to 574. The LjWRKYs can be divided into three subfamilies. Among them, the expression of LjWRKY (1/4/23/44) were significantly up-regulated under drought stress, whereas the expression of LjWRKY (21/25/65) were significantly down-regulated. Additionally, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis indicated that after drought stress, differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were enriched in plant hormone signal transduction pathway, the MAPK signaling pathway and biosynthesis of secondary metabolites pathway. In the MAPK pathway, there were 19 DEGs, 9 of which contained W-box regions, suggesting that they may be potential regulatory targets of LjWRKY TFs under drought stress.
Conclusion: These findings suggested that WRKY gene family may participate in the response to drought stress in L. japonicus. This study provides a scientific basis for the further development and functional validation of the WRKY gene family in L. japonicus.
Clinical trial number: Not applicable.
Keywords: Leonurus japonicus; Drought stress; Genome-wide analysis; WRKY family.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Plant material used in the study complies with relevant institutional, national, and international guidelines and legislation. Plant material used in the study is not wild species and also permission for the plant material was obtained. All experiments were performed according to institutional guidelines of Shandong University of technology, China. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and analysis of the WRKY gene family in Sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia) and their response to drought, salt, and alkali stress.BMC Genomics. 2025 May 2;26(1):437. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11646-2. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40316926 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of WRKY gene family in grain Amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus L.) under salinity and drought stresses.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Feb 28;25(1):265. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06270-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40021992 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of WRKY transcription factors in white pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) reveals evolution and patterns under drought stress.BMC Genomics. 2015 Dec 24;16:1104. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2233-6. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26704366 Free PMC article.
-
The physiological and molecular mechanisms of WRKY transcription factors regulating drought tolerance: A review.Gene. 2025 Feb 20;938:149176. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.149176. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Gene. 2025. PMID: 39694344 Review.
-
WRKY transcription factors: Key regulators in plant drought tolerance.Plant Sci. 2025 Oct;359:112647. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2025.112647. Epub 2025 Jul 5. Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40623547 Review.
References
-
- Shang X, Pan H, Wang X, He H, Li M. Leonurus japonicus Houtt.: ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and Pharmacology of an important traditional Chinese medicine. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;152(1):14–32. - PubMed
-
- Wei QH, Cao XX, Xu DF, Wang ST, Zhang JS, Zhang H. Anti-inflammatory labdane diterpenoids from the aerial parts of Leonurus japonicus. Phytochemistry. 2023;210:113646. - PubMed
-
- Wang C, Lv X, Liu W, Liu S, Sun Z. Uncovering the Pharmacological mechanism of motherwort (Leonurus japonicus Houtt.) for treating menstrual disorders: A systems Pharmacology approach. Comput Biol Chem. 2020;89:107384. - PubMed
-
- Zhou WS, Keyu C, Jian Y, Donghua F, Leran W, Ning S. Research progress of alkaloids in Leonurus japonicus. J Zhejiang Agric Sci. 2023;64(05):1230–5.
-
- Gong Y, Qiu Z, Hou W, Haq IU, Shafiq MR, Alharthi B. Characteristics of rapeseed (Brassica Rapa L.) genome DREB family demonstrate their roles in stress. Plant Stress 2024, 13.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

