Carboplatin, etoposide, atezolizumab, and bevacizumab in the first-line treatment of patients with extensive stage small-cell lung cancer: the GOIRC-01-2019 CeLEBrATE study
- PMID: 40341031
- PMCID: PMC12067786
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010694
Carboplatin, etoposide, atezolizumab, and bevacizumab in the first-line treatment of patients with extensive stage small-cell lung cancer: the GOIRC-01-2019 CeLEBrATE study
Abstract
Background: The addition of a programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor, either atezolizumab or durvalumab, to platinum-etoposide prolonged survival in a limited subset of patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). Preclinical studies demonstrated synergistic antitumor activity of combined vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and PD-L1 inhibition in SCLC. Since bevacizumab added to platinum-etoposide was safe and active in ES-SCLC, we investigated the efficacy of atezolizumab, bevacizumab, carboplatin, and etoposide as first-line treatment of ES-SCLC.
Methods: The CeLEBrATE study is an Italian multicentric single-arm phase II trial of carboplatin (area under the curve 5 ml/min), etoposide (100 mg/sqm), bevacizumab (7.5 mg/kg), and atezolizumab (1,200 mg) every 3 weeks (q3w) for four to six courses, followed by bevacizumab and atezolizumab maintenance q3w in patients with ES-SCLC and no contraindications to immunotherapy or antiangiogenic therapy. Patients with asymptomatic brain metastases were eligible. Prophylactic cranial irradiation and consolidation thoracic external radiotherapy were not permitted while on study treatment. Primary endpoint was overall survival (OS) rate at 1 year.
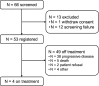
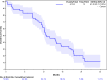
Results: 53 patients were enrolled (45.3% women, median age 65 years) and received at least one dose of study treatment. At a median follow-up time of 23.4 months (95% CI: 21.1 to 26.0), the 1-year OS rate was 61.8% (90% CI: 50.7% to 72.8%; p=0.04), with a median OS of 12.9 months (95% CI: 11.6 to 17.5). Median progression-free survival was 6.2 months (95% CI: 5.4 to 6.6) and objective response rate was 83.3% (95% CI: 69.8% to 92.5%). Grade 3-4 adverse events were reported in 34 patients (64.2%) leading to dose reductions in 24 (45.3%), and dose delays in 39 (73.9%) and 32 (69.6%) during the induction and maintenance phase, respectively. 19 (35.8%) treatment-related serious adverse events were reported.
Conclusion: The CeLEBrATE study met its primary objective demonstrating a signal of efficacy of bevacizumab, atezolizumab, carboplatin, and etoposide in the first-line treatment of patients with ES-SCLC.
Trial registration number: GOIRC-01-2019 ML41241, Eudract Number: 2019-003798-2.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; Combination therapy; Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor; Immunotherapy; Lung Cancer.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: GL received travel support by Roche. FM received advisory board fees from MSD, BMS, Takeda, Roche, AstraZeneca, and Regeneron. MT received speakers’ and consultants’ fees from AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, BMS, Novartis, Roche, MSD, Boehringer Ingelheim, Takeda, Amgen, Merck, Sanofi, Janssen, and Daiichi Sankyo. MT received institutional research grants from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Roche. MT received travel support from Amgen and Takeda. GP received Advisory Boards/Honoraria/Speakers’ fee/Consultant from: Amgen, AstraZeneca, BMS, Eli Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and Janssen. GP received unconditioned research support by: AstraZeneca, MSD, and Roche. CG received honoraria from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and Roche. AA has received honoraria for lectures and/or advisory board participation from BMS, AstraZeneca, MSD, Roche, Regeneron, Daiichi, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Takeda, Pfizer, and Novartis. All other authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
