Speckle-tracking echocardiographic abnormalities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40341169
- PMCID: PMC12060328
- DOI: 10.1186/s44348-025-00046-5
Speckle-tracking echocardiographic abnormalities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is known to be associated with cardiovascular disease due to shared risk factors and its impact on the cardiopulmonary vasculature. Speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE) is an effective tool for identifying subclinical, COPD-associated right ventricular (RV) and left ventricular (LV) dysfunction before conventional echocardiography can detect it. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature on STE in COPD are presented. A systematic search was conducted of PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane Library, and Science Direct for papers published between 2011 and March 2023, and bias was assessed using the STROBE tool. Eleven studies were included in the two-stage meta-analysis: first among 742 COPD cases, and then a case-control design with 507 COPD cases and 259 healthy controls. Of the 11 studies analyzed, 6 were dedicated to the assessment of RV strain, and 5 studies examined LV global longitudinal strain (GLS). Significant heterogeneity was observed in the STE parameters of COPD patients (I2 = 95%; mean effect size: -17.055 for LV GLS and -19.098 for RV free wall strain; Z = -35.809; P < 0.001) and between COPD patients and controls (I2 = 92%; mean effect size, 2.100; Z = 8.433; P < 0.0001). LV and RV STE parameters were lower in the COPD group than in the healthy control group. The two-dimensional STE parameters correlated with disease severity metrices such as the BODE (body mass index, airflow obstruction, dyspnea, and exercise) index and Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) classification, and they predicted mortality, hospitalization rates, and exercise tolerance in COPD patients. STE abnormalities are prevalent in COPD patients and can help identify subclinical LV and RV dysfunction. The presence of STE abnormalities helps in prognostication for COPD patients.
Keywords: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; Global longitudinal strain; Right ventricular free wall strain; Speckle-tracking echocardiography.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
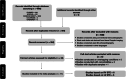
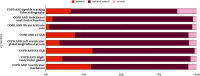
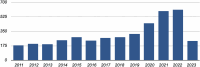



References
-
- Halpin DM, Celli BR, Criner GJ, Frith P, López Varela MV, Salvi S, et al. The GOLD Summit on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in low- and middle-income countries. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2019;23:1131–41. - PubMed
-
- Meghji J, Mortimer K, Agusti A, Allwood BW, Asher I, Bateman ED, et al. Improving lung health in low-income and middle-income countries: from challenges to solutions. Lancet. 2021;397:928–40. - PubMed
-
- Bhatt SP, Dransfield MT. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cardiovascular disease. Transl Res. 2013;162:237–51. - PubMed
-
- Divo M, Cote C, de Torres JP, Casanova C, Marin JM, Pinto-Plata V, et al. Comorbidities and risk of mortality in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;186:155–61. - PubMed
-
- Celeski M, Segreti A, Polito D, Valente D, Vicchio L, Di Gioia G, et al. Traditional and advanced echocardiographic evaluation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the forgotten relation. Am J Cardiol. 2024;217:102–18. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

