OTX2 expression contributes progression of gastric cancer in young adults
- PMID: 40341176
- PMCID: PMC12062444
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-99632-2
OTX2 expression contributes progression of gastric cancer in young adults
Abstract
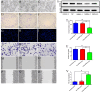
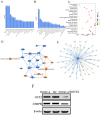
Gastric cancer of young adults is poorly differentiated and has a poor prognosis. However, there are few reports regarding the genetic alteration in gastric cancer of young adults. Bioinformatics methods were used to screen the key genes and signaling pathways of gastric cancer in young adults, and molecular biology techniques were used to verify the key proteins involved in the occurrence and development of gastric cancer in young adults. RNA expression profile microarray data of gastric cancer patients ≤ 45 years old and > 45 years old were downloaded from the TCGA database, and differentially expressed genes were screened by Limma package. GO analysis and KEGG enrichment analysis of DEG were performed in the Gene Function annotation database (DAVID). CytoHubba is used to construct protein interaction networks (PPI) and perform visual analysis to screen out core genes. We obtained 10 hub molecules, including FBXO44, FBXO6, HERC5, FBXL13, FBXO41, NT5E, BMP4, TRIM36, ACAN, ALPL by PPI network with MCODE. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis predicts TBX1, DFNB31, TGFBR3, FBXO44, SLC7A8, DNM1, KITLG, MSH5, MLLT3, DUSP5, ADAMTSL4, ACPP and TBX1 as the transcription factors directly regulated by OTX2. OTX2 had the highest positive expression rate in gastric cancer of young adults by immunohistochemistry. Interference with OTX2 expression inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion and promotes differentiation, apoptosis of NUGC-4 cells (from 35 year old female). Moreover, after interfering OTX2 expression, the downstream proteins and signaling Pathways of OTX2 in NUGC-4 were further analyzed by Transcriptome sequencing and Ingenuity Pathways Analysis. We found interference with OTX2 expression inhibits CEBPB expression and activates calcitriol by IPA analysis, thereby promoting differentiation of NUGC-4. Therefore, OTX2 plays important roles in restraining the differentiation and promoting progression of gastric cancer cells in young adults. Moreover, OTX2/CEBPB signal axis is likely to be a key molecular event in regulating the differentiation of gastric cancer cells in young adults.
Keywords: Differentiation; Gastric cancer; OTX2; Progression; Young adults.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

