Optimal transport reveals dynamic gene regulatory networks via gene velocity estimation
- PMID: 40341271
- PMCID: PMC12118989
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012476
Optimal transport reveals dynamic gene regulatory networks via gene velocity estimation
Abstract
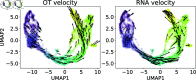
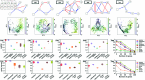
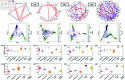
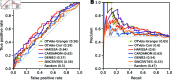
Inferring gene regulatory networks from gene expression data is an important and challenging problem in the biology community. We propose OTVelo, a methodology that takes time-stamped single-cell gene expression data as input and predicts gene regulation across two time points. It is known that the rate of change of gene expression, which we will refer to as gene velocity, provides crucial information that enhances such inference; however, this information is not always available due to the limitations in sequencing depth. Our algorithm overcomes this limitation by estimating gene velocities using optimal transport. We then infer gene regulation using time-lagged correlation and Granger causality via regularized linear regression. Instead of providing an aggregated network across all time points, our method uncovers the underlying dynamical mechanism across time points. We validate our algorithm on 13 simulated datasets with both synthetic and curated networks and demonstrate its efficacy on 9 experimental data sets.
Copyright: © 2025 Zhao et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures










Update of
-
Optimal transport reveals dynamic gene regulatory networks via gene velocity estimation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 16:2024.09.12.612590. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.12.612590. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: PLoS Comput Biol. 2025 May 8;21(5):e1012476. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012476. PMID: 39345416 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

