Muscone Attenuates Uveitis Through the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 40341311
- PMCID: PMC12068523
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.66.5.21
Muscone Attenuates Uveitis Through the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Purpose: Uveitis is an immune-mediated ocular disorder that poses a significant threat to vision, particularly among young and middle-aged adults. The treatment of uveitis is complicated by the presence of the blood-retinal barrier (BRB), which restricts the passage of large molecular drugs into the eye, thus limiting effective therapeutic options. The primary objective of this study is to identify a novel therapeutic agent capable of treating uveitis and explore its underlying mechanism.
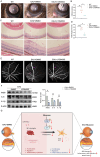
Methods: In this study, we used a mouse model of experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU) induced by interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ)-induced inflammatory BV2 cells. Evans blue and fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA) experiments were performed to evaluate the destruction of BRB. Silt lamp and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining were conducted to evaluate the inflammatory response. In vivo proteomics and Western blot were carried to investigate the underlying mechanisms.
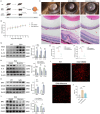
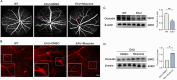
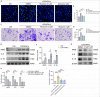
Results: Our study reveals that Muscone significantly alleviates EAU and restores the integrity of BRB. Moreover, Muscone treatment markedly downregulated inflammatory factors within the retinas and BV2 cells. In vivo proteomic combined with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) has elucidated that Muscone exerts its anti-inflammatory effects by modulating the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. Moreover, by using LY294002 to specifically inhibit PI3K, we observed a marked decrease in inflammatory phenotype and BRB destruction of EAU.
Conclusions: In summary, this study establishes the protective efficacy of Muscone against the progression of EAU and provides insights into the molecular mechanisms responsible for its therapeutic action.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sinomenine alleviates experimental autoimmune uveitis in rats: Possible involvement of PI3K/AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 5;996:177571. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177571. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40180267
-
A cell-permeable peptide inhibitor of p55PIK signaling alleviates ocular inflammation in mouse models of uveitis.Exp Eye Res. 2020 Oct;199:108180. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2020.108180. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Exp Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 32777209
-
Aminooxy-Acetic Acid Inhibits Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis by Modulating the Balance between Effector and Regulatory Lymphocyte Subsets.Curr Mol Med. 2020;20(8):624-632. doi: 10.2174/1566524020666200211112219. Curr Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32072910
-
Apremilast Regulates the Teff/Treg Balance to Ameliorate Uveitis via PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 Signaling Pathway.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 17;11:581673. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.581673. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33281814 Free PMC article.
-
Small-molecule antagonist of VLA-4 (GW559090) attenuated neuro-inflammation by targeting Th17 cell trafficking across the blood-retinal barrier in experimental autoimmune uveitis.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Feb 18;18(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02080-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 33602234 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

