A correlational study of plasma galectin-3 as a potential predictive marker of postoperative delirium in patients with acute aortic dissection
- PMID: 40341412
- PMCID: PMC12062433
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-98858-4
A correlational study of plasma galectin-3 as a potential predictive marker of postoperative delirium in patients with acute aortic dissection
Abstract
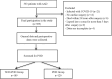
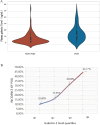
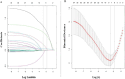
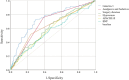
This study aimed to demonstrate whether plasma galectin-3 could predict the development of postoperative delirium (POD) in patients with acute aortic dissection (AAD). Prospective, observational study. Cardiac surgery intensive care unit. Consecutive patients who were diagnosed with AAD and operated at the Cardiac Medical Center of Fujian Province between December 2020 and December 2022. Patients were classiffed into two groups according to the Confusion Assessment Method for the Intensive Care Unit: POD group and NON-POD group. Each patient's plasma was tested before emergency surgery. Baseline demographic data and preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative clinical data were collected. The short-term clinical outcomes were followed up daily. The rate of POD was calculated. The risk factors for POD were analyzed through univariate analysis and multivariate logistic regression. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to assess the ability of plasma galectin-3 to predict POD. A total of 309 study subjects were included in this study, and the rate of POD was 38.8%. Patients with AAD were categorized into the POD and NON-POD cohorts postoperatively based on their CAM-ICU scores. There was no statistically significant difference in the baseline characteristics between the two groups (P > 0.05). However, patients in the POD group had significantly elevated plasma galectin-3 levels (P < 0.001). The ROC curves showed that plasma galectin-3 had a sensitivity of 72.5% and a specificity of 70.9% as a potential biomarker for the diagnosis of POD. The critical value of plasma galectin-3 for diagnosing POD was 9.18 ng/mL. Plasma galectin-3 levels remained an independent predictor of POD after controlling for different variables (P < 0.001). Elevated plasma galectin-3 levels are associated with an increased risk of POD. Plasma galectin-3 may be a prospective biomarker for predicting POD.
Keywords: Aortic dissection; Galectin-3; Postoperative delirium.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma interleukin-6 is a potential predictive biomarker for postoperative delirium among acute type a aortic dissection patients treated with open surgical repair.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2021 May 27;16(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s13019-021-01529-4. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2021. PMID: 34044881 Free PMC article.
-
[Predictive value of leukocyte derived markers for postoperative delirium after cardiac valve surgery].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Jul;36(7):728-733. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240227-00164. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 39223888 Chinese.
-
Risk Factors for Postoperative Delirium in Type A Aortic Dissection Patients: A Retrospective Study.Med Sci Monit. 2019 May 18;25:3692-3699. doi: 10.12659/MSM.913774. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31102507 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative electroencephalography predicts postoperative delirium in adult cardiac surgical patients from a prospective observational study.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):31101. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82422-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39730694 Free PMC article.
-
Independent Predictors of the Duration and Overall Burden of Postoperative Delirium After Cardiac Surgery in Adults: An Observational Cohort Study.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2017 Dec;31(6):1966-1973. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2017.03.042. Epub 2017 Mar 31. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2017. PMID: 28711314
References
-
- Mangum, K. D. & Farber, M. A. Genetic and epigenetic regulation of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Clin. Genet.97(6), 815–826 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Swarbrick, C. J. & Partridge, J. S. L. Evidence-based strategies to reduce the incidence of postoperative delirium: A narrative review. Anaesthesia77(Suppl), 1 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Lee, D. H. et al. Postoperative delirium in patients receiving hip bipolar hemiarthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: The risk factors and further clinical outcomes. J. Arthroplasty38(4), 737–742 (2023). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

