Massively parallel jumping assay decodes Alu retrotransposition activity
- PMID: 40341501
- PMCID: PMC12062377
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59347-4
Massively parallel jumping assay decodes Alu retrotransposition activity
Abstract
The human genome contains millions of copies of retrotransposons that are silenced but many of these copies have potential to become active if mutated, having phenotypic consequences, including disease. However, it is not thoroughly understood how nucleotide changes in retrotransposons affect their jumping activity. Here, we develop a massively parallel jumping assay (MPJA) that tests the jumping potential of thousands of transposons en masse. We generate a nucleotide variant library of four Alu retrotransposons containing 165,087 different haplotypes and test them for their jumping ability using MPJA. We found 66,821 unique jumping haplotypes, allowing us to pinpoint domains and variants vital for transposition. Mapping these variants to the Alu-RNA secondary structure revealed stem-loop features that contribute to jumping potential. Combined, our work provides a high-throughput assay that assesses the ability of retrotransposons to jump and identifies nucleotide changes that have the potential to reactivate them in the human genome.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: N.M. is a Cofounder and the Chief Scientific Officer for Regel Therapeutics Inc. N.A. is a Cofounder and on the scientific advisory board of Regel Therapeutics Inc. N.A. received funding from BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
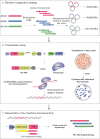

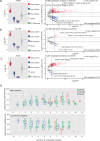
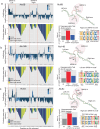
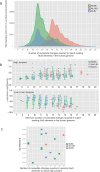
Update of
-
Massively parallel jumping assay decodes Alu retrotransposition activity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 19:2024.04.16.589814. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.16.589814. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 May 9;16(1):4310. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59347-4. PMID: 38659854 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UM1 HG009408/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM142112/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1HG009408/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)
- UM1HG011966/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)
- UM1 HG011966/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

