A green one pot approach for extracting free fatty acids from microalgae
- PMID: 40341704
- PMCID: PMC12062437
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-00235-8
A green one pot approach for extracting free fatty acids from microalgae
Abstract
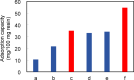
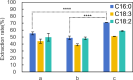
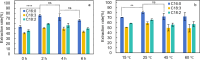
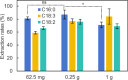
A green one pot approach for extracting free fatty acids (FFAs) from microalgae has been established by combining bead milling and anion resin adsorption. In which, microalgae were initially pretreated by 10 min of bead milling for cell disruption and release of FFAs. Strong base anion resin was added in situ and solid-solid extraction was conducted for another 30 min. After further solid-liquid extraction was carried out at 25 °C for 2 h, FFAs were eluted with ethanol and acetic acid. For example, commercially available Spirulina platensis powder was quantitatively analyzed to afford the extraction rates of 87%, 77%, and 76% for palmitic acid, linolenic acid, and linoleic acid, respectively. Further, 7.0 mg/g of the three major FFAs from 0.25 g of Spirulina platensis have been determined. To scale up, 1 g of Spirulina platensis was applied to afford 6.3 mg of the three major FFAs with 8 g resins. Moreover, the extraction rates of major FFAs were determined to be 68%-92% for Picochlorum sp. and 53%-63% for mixed microalgae, respectively. It is suggested that this protocol without utilization of toxic organic solvents will benefit operators who engage in extracting FFAs in microalgae and producing FFA derivative products from microalgae.
Keywords: Bead milling; Free fatty acids; Green process; Microalgae; Strong base anion resin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Wang, X. et al. Lipidomic analysis of microalgae and its application in microalgae cultivation and alternative liquid biofuel production. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 10.1007/s13399-024-05510-8 (2024).
-
- Balduyck, L. et al. Inhibition of lipolytic reactions during wet storage of T-Isochrysis lutea biomass by heat treatment. Algae Res.38. 10.1016/j.algal.2018.101388 (2019).
-
- Balduyck, L. et al. Integrity of the microalgal cell plays a major role in the lipolytic stability during wet storage. Algae Res.25, 516–524. 10.1016/j.algal.2017.06.013 (2017).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

