Scaffold-level genome assembly of Fusarium neocosmosporiellum strain CA18-1
- PMID: 40341731
- PMCID: PMC12062361
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-025-05073-x
Scaffold-level genome assembly of Fusarium neocosmosporiellum strain CA18-1
Abstract
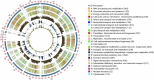
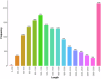
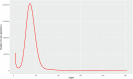
Fusarium neocosmosporiellum causes alfalfa root rot, leading to significant economic losses. To explore the genetics of F. neocosmosporiellum, strain CA18-1 was isolated from infected alfalfa roots and subjected to whole-genome analysis. A scaffold-level reference genome of strain CA18-1 was assembled using both Nanopore long-read and Illumina short-read sequencing technologies. The assembled genome measured 63,424,297 base pairs (bp) in size, with a contig N50 of 6,480,858 bp and a contig N90 of 3,230,245 bp. A total of 10,486,459 bp repeat sequences and 28,006 protein-coding genes were predicted, of which 15,389 were functionally annotated. This study enhances our understanding of the genetic basis for F. neocosmosporiellum's pathogenicity, providing a foundation for future studies on disease control and fungal evolution.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome sequence of Fusarium oxysporum strain ByF01, the causal agent of root rot of Knoxia roxburghii in China.BMC Genom Data. 2024 Jun 14;25(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12863-024-01242-w. BMC Genom Data. 2024. PMID: 38877406 Free PMC article.
-
Auxiliary rapid identification of pathogenic and antagonistic microorganisms associated with Coptis chinensis root rot by high-throughput sequencing.Sci Rep. 2021 May 27;11(1):11141. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90489-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34045546 Free PMC article.
-
Citric acid impairs type B trichothecene biosynthesis of Fusarium graminearum but enhances its growth and pigment biosynthesis: transcriptomic and proteomic analyses.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 Jun 18;91(6):e0153124. doi: 10.1128/aem.01531-24. Epub 2025 May 14. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40366181 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagavathiannan, M. V., Gulden, R. H., Begg, G. S. & Van Acker, R. C. The demography of feral alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) populations occurring in roadside habitats in Southern Manitoba, Canada: implications for novel trait confinement. Environmental science and pollution research international17, 1448–1459, 10.1007/s11356-010-0330-2 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Mielmann, A. The utilisation of lucerne (Medicago sativa): a review. British Food Journal115, 590–600 (2013).
-
- Chen, J., Guo, Z. W., Pan, C. Q., Xiang, P. & Liu, D. W. Research status of alfalfa diseases, insect pests and weeds. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science01, 1–14 (2022).
-
- Fang, X. L., Zhang, C. X. & Nan, Z. B. Research advances in Fusarium root rot of alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Acta Prataculturae Sinica28, 169–183 (2019).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

