Control of replication and gene expression by ADP-ribosylation of DNA in Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 40341764
- PMCID: PMC12170906
- DOI: 10.1038/s44318-025-00451-y
Control of replication and gene expression by ADP-ribosylation of DNA in Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Control of replication and gene expression by ADP-ribosylation of DNA in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.EMBO J. 2025 Aug;44(15):4406. doi: 10.1038/s44318-025-00491-4. EMBO J. 2025. PMID: 40562877 Free PMC article.
Abstract
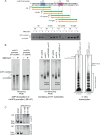
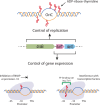
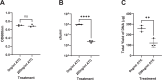
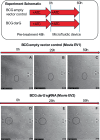
Mycobacterium tuberculosis maintains long-term infections characterised by the need to regulate growth and adapt to contrasting in vivo environments. Here we show that M. tuberculosis complex bacteria utilise reversible ADP-ribosylation of single-stranded DNA as a mechanism to coordinate stationary phase growth with transcriptional adaptation. The DNA modification is controlled by DarT, an ADP-ribosyltransferase, which adds ADP-ribose to thymidine, and DarG, which enzymatically removes this base modification. Using darG-knockdown M. bovis BCG, we map the first DNA ADP-ribosylome from any organism. We show that inhibition of replication by DarT is reversible and accompanied by extensive ADP-ribosylation at the origin of replication (OriC). In addition, we observe ADP-ribosylation across the genome and demonstrate that ADP-ribose-thymidine alters the transcriptional activity of M. tuberculosis RNA polymerase. Furthermore, we demonstrate that during stationary phase, DarT-dependent ADP-ribosylation of M. tuberculosis DNA is required to optimally induce expression of the Zur regulon, including the ESX-3 secretion system and multiple alternative ribosome proteins. Thus, ADP-ribosylation of DNA can provide a mechanistic link through every aspect of DNA biology from replication to transcription to translation.
Keywords: ADP-ribosylation; ADPr-Seq; DNA Modification; PARP; Transcription Regulation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Development and characterization of recombinant ADP-ribose binding reagents that allow simultaneous detection of mono and poly ADP-ribose.J Biol Chem. 2024 Sep;300(9):107609. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107609. Epub 2024 Jul 27. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39074634 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Inhibitors for Bacterial Arr Enzymes ADP-Ribosylating and Inactivating Rifamycin Antibiotics.ACS Chem Biol. 2025 Jul 18;20(7):1584-1593. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.5c00164. Epub 2025 Jun 13. ACS Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 40509881
-
Molecular basis for DarT ADP-ribosylation of a DNA base.Nature. 2021 Aug;596(7873):597-602. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03825-4. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Nature. 2021. PMID: 34408320
-
Interferon-induced ADP-ribosylation: technical developments driving ICAB discovery.Biosci Rep. 2025 Mar 14;45(3):BSR20240986. doi: 10.1042/BSR20240986. Biosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40014063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banerjee R, Rudra P, Prajapati RK, Sengupta S, Mukhopadhyay J (2014) Optimization of recombinant Mycobacterium tuberculosis RNA polymerase expression and purification. Tuberculosis 94:397–404 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

