Efficacy and safety of cinobufacin-based combination therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 40342028
- PMCID: PMC12062485
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-02501-7
Efficacy and safety of cinobufacin-based combination therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Primary liver cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors with a rising incidence in recent years. In China, it ranks as the fourth most prevalent malignancy. Although surgery is the primary treatment, many advanced-stage patients are ineligible due to late diagnosis, rapid progression, or other contraindications. Targeted therapy, chemotherapy, and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) are common non-surgical approaches, but these often result in significant side effects such as gastrointestinal reactions, bone marrow suppression, and high recurrence rates. In this context, integrative treatment with traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has shown promise. Cinobufacin, a TCM drug developed in China, has demonstrated superior efficacy and safety when combined with Western treatments in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis by searching PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, CNKI, WanFang Data, VIP, and the Chinese Biomedical Literature Database (CBM) for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing cinobufacin combined with conventional Western treatments to Western treatments alone in advanced HCC patients. The search covered all databases up to December 30, 2024. Statistical analyses were performed using Stata 15.0, and Review Manager.
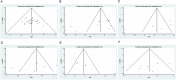
Results: A total of 30 studies were included in the meta-analysis. Cinobufacin combination therapy significantly improved the disease control rate (DCR, OR = 2.49, 95% CI 2.01 to 3.07), reduced alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels (SMD = - 1.86, 95% CI - 2.58 to - 1.13), alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels (SMD = - 1.66, 95% CI - 2.48 to - 0.83), and total bilirubin (TBIL) levels (SMD = - 1.82, 95% CI - 2.36 to - 1.28). It also increased white blood cell (WBC) counts (SMD = 0.58, 95% CI 0.06 to 1.11) and improved Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) scores (SMD = 1.24, 95% CI 0.93 to 1.56). Funnel plots and sensitivity analyses confirmed the robustness of the results.
Conclusion: Cinobufacin combined with Western treatments significantly improves clinical efficacy, reduces adverse drug reactions, and enhances the quality of life for patients with advanced HCC.
Keywords: Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma; Cinobufacin; Efficacy; Meta-analysis; Safety.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Informed consent: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Li YK, Wu S, Wu YS, Zhang WH, Wang Y, Li YH, et al. Portal venous and hepatic arterial coefficients predict post-hepatectomy overall and recurrence-free survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024;11:1389–402. 10.2147/JHC.S462168. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
