Cell-Penetrating Peptide-Based Triple Nanocomplex Enables Efficient Nuclear Gene Delivery in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
- PMID: 40342143
- PMCID: PMC12235220
- DOI: 10.1002/bit.29019
Cell-Penetrating Peptide-Based Triple Nanocomplex Enables Efficient Nuclear Gene Delivery in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Abstract
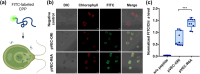
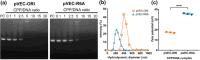
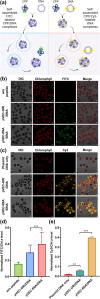
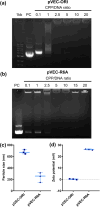
Microalgae are a promising solution for mitigating climate change due to their ability to capture greenhouse gases and produce renewable materials. However, their effective application is often hindered by barriers that necessitate advances in genetic engineering to improve photosynthesis and productivity. One major obstacle is the microalgal cell wall, which complicates the delivery of genetic material into these organisms. To address these challenges, we developed a novel triple nanocomplex system integrating cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs), nuclear localization signal (NLS) peptides, and plasmid DNA. This system allows simple preparation while achieving efficient nuclear translocation of plasmid DNA. We evaluated two CPPs, pVEC-ORI and pVEC-R6A, for their efficacy in facilitating intracellular transfer of DNA into wild-type Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cells. Notably, pVEC-R6A demonstrated a 6.88-fold increase in efficiency compared to pVEC-ORI, despite the presence of thick cell walls. The optimal CPP:DNA ratio for stable nanocomplex formation was determined to be 5:1 for pVEC-ORI and 10:1 for pVEC-R6A. By incorporating the simian virus 40 (SV40) NLS into CPP/DNA nanocomplexes, we successfully directed the localization of plasmid DNA into the nucleus. Our findings indicate that this simple and efficient DNA delivery system has significant potential as a tool to advance microalgal synthetic biology.
Keywords: SV40; cell‐penetrating peptide; gene delivery; microalgae; nanocomplex; nuclear localization signal; pVEC.
© 2025 The Author(s). Biotechnology and Bioengineering published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural basis for nuclear import of adeno-associated virus serotype 6 capsid protein.J Virol. 2025 Jan 31;99(1):e0134524. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01345-24. Epub 2024 Dec 18. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 39692478 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient photoproduction of a high-value sesquiterpene pentalenene from the green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Plant J. 2025 Jul;123(2):e70354. doi: 10.1111/tpj.70354. Plant J. 2025. PMID: 40680273
-
The Lived Experience of Autistic Adults in Employment: A Systematic Search and Synthesis.Autism Adulthood. 2024 Dec 2;6(4):495-509. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0114. eCollection 2024 Dec. Autism Adulthood. 2024. PMID: 40018061 Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Organic Synthesis Away from Equilibrium: Contrathermodynamic Transformations Enabled by Excited-State Electron Transfer.Acc Chem Res. 2024 Jul 2;57(13):1827-1838. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.4c00227. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Acc Chem Res. 2024. PMID: 38905487 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

