Paraoxonase 1 Enzyme Activity in Patients With Isolated Coronary Artery Ectasia
- PMID: 40342642
- PMCID: PMC12059976
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.83703
Paraoxonase 1 Enzyme Activity in Patients With Isolated Coronary Artery Ectasia
Abstract
Objective: Paraoxonase 1 (PON1) is an organophosphate ester hydrolase associated with high-density lipoprotein (HDL). The recently emphasized function of PON1 activity is its antiatherogenic activity. PON1 is always found together with HDL in plasma, and PON1 is responsible for the protective effect of HDL against low-density lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation. Considering this role in cardiovascular diseases and its antioxidant properties, PON1 activity may be a valuable biomarker in predicting coronary artery ectasia (CAE), whose pathogenesis has not yet been fully elucidated. The aim was to reveal the relationship between PON1 activity and isolated CAE.
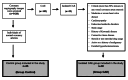
Method: This prospective case-control study's population comprises 5240 patients who underwent coronary angiography between December 2009 and April 30, 2010. Thirty patients with isolated CAE (Group CAE) and 25 volunteers with normal coronary arteries (Group Control) who met the inclusion criteria were included in the study. The sociodemographic, clinical, and anatomical characteristics and lipid profiles of the patients were analyzed. Groups CAE and control were compared in terms of PON1 activity levels.
Results: There was no significant difference between Group CAE (n=30) and Group Control (n=25) in terms of sociodemographic and clinical characteristics (p>0.05). There was ectasia in a single coronary artery in 19 patients (63.3%). The right coronary artery (RCA) was ectasian in 17 patients (38.6%) and was the most affected vessel. According to the Markis classification, the most common type of ectasia was type IV ectasia, which was seen in 14 patients (46.7%). When lipid profiles were compared, no difference was observed between the groups. PON1 activity levels were significantly lower in the CAE group than in the control group (Group CAE=127.5 U/L; Group Control=177.0 U/L; p<0.001).
Conclusions: This study's findings suggest a significant correlation between low PON1 activity levels and the development of isolated CAE, suggesting that PON1 activity may play a potential role in the pathophysiology of CAE. Based on the association demonstrated between isolated CAE and PON1 activity in our study, future research may investigate the potential use of PON1 as a biomarker.
Keywords: coronary artery angiography; coronary artery anomaly; coronary artery disease; coronary artery ectasia; paraoxonase 1.
Copyright © 2025, Aslan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Dr. Siyami Ersek Hospital Ethics Committee issued approval 4869. The study titled “Relationship Between Paraoxonase Enzyme Activity in Patients with Isolated Coronary Ectasia” was approved by the ethics committee of Dr. Siyami Ersek Hospital, dated 06.07.2009 and numbered 4869. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Among Ectasia Patients with Coexisting Coronary Artery Disease, TIMI Frame Count Correlates with Ectasia Size and Markis Type IV Is the Commonest.Cardiol Res Pract. 2015;2015:282170. doi: 10.1155/2015/282170. Epub 2015 Feb 3. Cardiol Res Pract. 2015. PMID: 25705544 Free PMC article.
-
A new inflammatory marker: elevated eosinophil-tolymphocyte ratio associated with presence and severity of isolated coronary artery ectasia.Cardiovasc J Afr. 2020 Sep/Oct;31(5):227-235. doi: 10.5830/CVJA-2019-049. Epub 2020 Oct 2. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2020. PMID: 33015703 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of prevalence and risk factors of isolated coronary artery ectasia: A 5-year double-center retrospective study in Yazd, Iran.Caspian J Intern Med. 2024 Spring;15(2):244-250. doi: 10.22088/cjim.15.2.244. Caspian J Intern Med. 2024. PMID: 38807718 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated oxidative stress markers as independent predictors of isolated coronary artery ectasia.Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej. 2025 Mar;21(1):67-72. doi: 10.5114/aic.2025.148148. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej. 2025. PMID: 40182090 Free PMC article.
-
Ratio of Serum Aspartate to Alanine Aminotransferase as a Marker of Isolated Coronary Artery Ectasia and its Severity.Heart Int. 2020 Jul 31;14(1):43-48. doi: 10.17925/HI.2020.14.1.43. eCollection 2020. Heart Int. 2020. PMID: 36277666 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Prevalence and angiographic characteristics of coronary artery ectasia among patients with coronary artery disease: a retrospective analysis between 2014 and 2022. Yuan M, Li R, Wu Q, Chen Q. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2023;261:165–171. - PubMed
-
- The relationship between oxidative stress and coronary artery ectasia. Sezen Y, Bas M, Polat M, et al. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20865680/ Cardiol J. 2010;17:488–494. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous