MiR-335-5p Escaped from CircKIAA0586 Adsorption Contributes to Mechanical Overloading-Induced Cartilage Degeneration by Targeting Lymphoid-Specific Helicase
- PMID: 40342810
- PMCID: PMC12059312
- DOI: 10.34133/research.0694
MiR-335-5p Escaped from CircKIAA0586 Adsorption Contributes to Mechanical Overloading-Induced Cartilage Degeneration by Targeting Lymphoid-Specific Helicase
Abstract
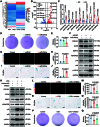
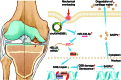
Mechanical overload is a critical contributor to cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis (OA) pathogenesis. Circular RNA (circRNA) is expected to provide a long-lasting therapy for OA. However, the involvement of the circRNA-associated competitive endogenous RNA network in chondrocyte senescence induced by mechanical overloading remains unestablished. A mechanical overloading-induced chondrocyte senescence model in human primary chondrocytes is constructed, and differences in the expression of circRNAs and miRNAs were analyzed. The biological roles of circKIAA0586/miR-335-5p in chondrocyte senescence and OA progression under mechanical overloading and its downstream targets were determined using gain- and loss-of-function experiments in various biochemical assays in human chondrocytes. The in vivo effects of circKIAA0586 overexpression were also determined in destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM) OA mice and aged spontaneous OA mice. The mechanical overloading-induced chondrocyte senescence was aggravated by miR-335-5p or circKIAA0586 knockdown. Accumulated DNA damage response was observed following mechanical overloading, which reduced after miR-335-5p inhibition or circKIAA0586 supplementation. MiR-335-5p was regulated by circKIA0586 adsorption. HELLS was prominently down-regulated following mechanical overloading treatment. Moreover, miR-335-5p bound to lymphoid-specific helicase (HELLS) mRNA during mechanical overloading was demonstrated to mediate the nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway, thereby inducing DNA damage and senescence. In addition, the senescence delaying and cartilage protective functions of circKIAA0586 and HELLS were validated in DMM OA mice and aged spontaneous OA mice. Our findings suggest that miR-335-5p, which escapes circKIAA0586 adsorption, facilitates mechanical overloading-induced chondrocyte senescence and OA progression by impairing the NHEJ pathway through HELLS inhibition. Overall, targeting circKIAA0586/miR-335-5p/HELLS signaling provides a novel therapeutic approach for OA.
Copyright © 2025 Haoyu Xie et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Quicke JG, Conaghan PG, Corp N, Peat G. Osteoarthritis year in review 2021: Epidemiology & therapy. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2022;30(2):196–206. - PubMed
-
- Safiri S, Kolahi AA, Smith E, Hill C, Bettampadi D, Mansournia MA, Hoy D, Ashrafi-Asgarabad A, Sepidarkish M, Almasi-Hashiani A, et al. . Global, regional and national burden of osteoarthritis 1990-2017: A systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study 2017. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(6):819–828. - PubMed
-
- Hunter DJ, Bierma-Zeinstra S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393(9991):1745–1759. - PubMed
-
- Visser AW, Mutsert R, Cessie S, Heijer M, Rosendaal FR, Kloppenburg M, Group NEOS . The relative contribution of mechanical stress and systemic processes in different types of osteoarthritis: The NEO study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(10):1842–1847. - PubMed
-
- Andriacchi TP, Favre J. The nature of in vivo mechanical signals that influence cartilage health and progression to knee osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2014;16(11):463. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

