Role of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in the Self-Renewal, Differentiation, and Immunomodulation of Adult Stem Cells
- PMID: 40342843
- PMCID: PMC12056294
- DOI: 10.4110/in.2025.25.e1
Role of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in the Self-Renewal, Differentiation, and Immunomodulation of Adult Stem Cells
Abstract
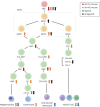
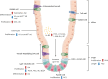
Adult stem cells are a rare population of undifferentiated cells present in almost all body tissues. Depending on their location, stem cells can differentiate into various tissue types, primarily contributing to maintenance, repair, and immune system regulation. Stem cell therapies have significant potential in regenerative medicine and treatment of inflammatory diseases. However, many factors must be considered for successful clinical commercialization, including enhancing therapeutic potential, ensuring product differentiation, and optimizing the manufacturing process for large-scale production. The development of sophisticated regulatory mechanisms may enhance therapeutic applications. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is expressed in all adult stem cells, and its activation and function are tightly regulated. Understanding the role and regulation of AhR is crucial for developing effective stem cell therapies. This review examines the role of the AhR in regulating the fundamental characteristics of adult stem cells, which may contribute to advancing adult stem cell therapies.
Keywords: Adult stem cells; Aryl hydrocarbon receptor; Cell differentiation; Cell self-renewal.
Copyright © 2025. The Korean Association of Immunologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Barker N. Adult intestinal stem cells: critical drivers of epithelial homeostasis and regeneration. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:19–33. - PubMed
-
- Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S, Marshak DR. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284:143–147. - PubMed
-
- Caplan AI. Mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 1991;9:641–650. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

