This is a preprint.
Consensus Recommendations for Hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate MRI Multi-center Human Studies
- PMID: 40342865
- PMCID: PMC12060990
Consensus Recommendations for Hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate MRI Multi-center Human Studies
Update in
-
Consensus recommendations for hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate MRI multi-center human studies.Magn Reson Med. 2025 Oct;94(4):1386-1400. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30570. Epub 2025 Jun 16. Magn Reson Med. 2025. PMID: 40523079 Free PMC article.
Abstract
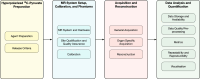
Magnetic resonance imaging of hyperpolarized (HP) [1-13C]pyruvate allows in-vivo assessment of metabolism and has translated into human studies across diseases at 15 centers worldwide. Consensus on best practice for multi-center studies is required to develop clinical applications. This paper presents the results of a 2-round formal consensus building exercise carried out by experts with HP [1-13C]pyruvate human study experience. Twenty-nine participants from 13 sites brought together expertise in pharmacy methods, MR physics, translational imaging, and data-analysis; with the goal of providing recommendations and best practice statements on conduct of multi-center human studies of HP [1-13C]pyruvate MRI. Overall, the group reached consensus on approximately two-thirds of 246 statements in the questionnaire, covering 'HP 13C-Pyruvate Preparation', 'MRI System Setup, Calibration, and Phantoms', 'Acquisition and Reconstruction', and 'Data Analysis and Quantification'. Consensus was present across categories, examples include that: (i) different HP pyruvate preparation methods could be used in human studies, but that the same release criteria have to be followed; (ii) site qualification and quality assurance must be performed with phantoms and that the same field strength must be used, but that the rest of the system setup and calibration methods could be determined by individual sites;(iii) the same pulse sequence and reconstruction methods were preferable, but the exact choice should be governed by the anatomical target; (iv) normalized metabolite area-under-curve (AUC) values and metabolite AUC were the preferred metabolism metrics. The work confirmed areas of consensus for multi-center study conduct and identified where further research is required to ascertain best practice.
Conflict of interest statement
DV, PL, and JG receive research grant funding from GE Healthcare. DV, RB, JS and SP are advisors for NVision Imaging Technologies. JAB is on the scientific advisory board for NVision, and he receives research funding from Siemens. JHA is the owner of Polarize, a company that sells instrumentation for hyperpolarization. FG receives research support from GE Healthcare and grant funding from NVision and AstraZeneca. KRK is a founder of Atish Technologies and a member of the scientific advisory boards of Nvision Imaging Technologies, Imaginostics and Mi2. KRK hold patents related to imaging and modulation of cellular metabolism. SP is an advisor for QUIBIM Ltd, and Cheif Medical Officer for Gold Standard Phantoms. CV receives research support from Siemens.
Figures
References
-
- Fitch K, Bernstein SJ, Aguilar MD, et al. The RAND/UCLA Appropriateness Method User’s Manual. RAND Corporation; 2001.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous