Meta-analysis of budesonide and surfactant combination for the prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm neonates based on gestational age
- PMID: 40342892
- PMCID: PMC12058727
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2025.1518957
Meta-analysis of budesonide and surfactant combination for the prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm neonates based on gestational age
Abstract
Background: Budesonide, an inhaled corticosteroid, and surfactant, a substance that lowers surface tension in the lungs, are both used to prevent Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD). This meta-analysis evaluates the effectiveness of combining budesonide and surfactant in preventing BPD in preterm neonates compared to surfactant alone.
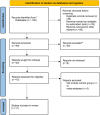
Method: A comprehensive search of electronic databases, including PubMed, Scopus, Google Scholar, CNKI, and Embase, was conducted from their inception up to August 30, 2024. The focus was on evaluating the combination of Budesonide and surfactant for the prevention of BPD in preterm neonates. This assessment involved calculating ORs and their 95% CIs to determine the treatment's effectiveness. The primary outcomes measured were the incidence of BPD and mortality rates, while secondary outcomes included the rates of intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), sepsis, neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), and pneumothorax.
Results: This research, combining a meta-analysis and observational data, indicates that Budesonide-Surfactant therapy significantly reduces BPD in preterm neonates with NRDS, regardless of gestational age. Additional benefits, including decreased mortality (in ≥27 gestational weeks), NEC, PDA, ROP, and Sepsis, were observed in the observational study, though pneumothorax increased in the ≥27 gestational weeks group. The meta-analysis corroborated reductions in BPD, PDA, and mortality (in ≥27 gestational weeks), supporting the potential of Budesonide-Surfactant to improve outcomes in preterm infants.
Conclusions: The intratracheal administration of pulmonary surfactants combined with budesonide was associated with a reduction in the incidence of BPD, mortality, and PDA. Although the prevalence of ROP, NEC, IVH, and sepsis was lower in the test group compared to the control group, these differences did not reach statistical significance. These findings suggest that the combined use of budesonide and surfactant is effective in preventing BPD and mortality, as well as in reducing certain secondary outcomes.
Keywords: bronchopulmonary dysplasia; budesonide; controlled trials; preterm neonates; pulmonary surfactant.
© 2025 Ekraminasab, Noorishadkam, Neamatzadeh, Lookzadeh, Mirjalili, Mazaheri and Shams.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


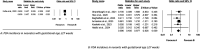
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

