Multi-target neuroprotection by dl-PHPB in APP/PS1 mice: a proteomic analysis
- PMID: 40343003
- PMCID: PMC12058804
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1554168
Multi-target neuroprotection by dl-PHPB in APP/PS1 mice: a proteomic analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Dl-PHPB [potassium 2-(1-hydroxypentyl) benzoate] demonstrates robust neuroprotective effects in preclinical models of Alzheimer's disease (AD), significantly ameliorating cognitive deficits and pathological hallmarks. However, the underlying mechanism remains largely unclear. The current study primarily focused on elucidating dl-PHPB's neuroprotective mechanisms and identifying potential targets in preclinical AD models.
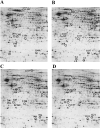
Methods: Comparative proteomic analyses were performed on APP/PS1 mice orally administered either dl-PHPB (30 mg/kg) or vehicle daily for 3 months, alongside vehicle-treated wild-type (WT) non-transgenic littermates as controls. Total proteins were separated using two dimensional difference gel electrophoresis, and differentially expressed protein spots were identified via LC-MS/MS.
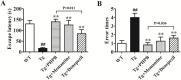
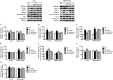
Results and discussion: Our results revealed 11 altered proteins in the cortex and 10 in the hippocampus between the WT and APP/PS1 groups treated with vehicle. Following dl-PHPB treatment, 12 differentially expressed proteins were identified in the cortex and 9 in the hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice. These proteins are primarily involved in energy metabolism, neuronal structure, protein trafficking, inflammatory and oxidative responses, and amyloid β (Aβ) and Tau processes, among which several proteins were validated as potential therapeutic targets. Notably, the expression levels of cofilin-2 and VDAC1 in APP/PS1 mice were restored to near-normal levels by the treatment with dl-PHPB, memantine, or donepezil, and further clinical validation is required to establish their utility as AD biomarkers for therapeutic efficacy.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; LC-MS/MS; biomarker; dl-PHPB; proteomics.
Copyright © 2025 Sun, Bai, Yang, Feng, Sun, Xian and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
Author YS was employed by Beijing Handian Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potassium 2-(1-hydroxypentyl)-benzoate improves memory deficits and attenuates amyloid and τ pathologies in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 Aug;350(2):361-74. doi: 10.1124/jpet.114.213140. Epub 2014 Jun 3. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014. PMID: 24893984
-
Potassium 2-(1-hydroxypentyl)-benzoate promotes long-term potentiation in Aβ1-42-injected rats and APP/PS1 transgenic mice.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014 Jul;35(7):869-78. doi: 10.1038/aps.2014.29. Epub 2014 May 26. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014. PMID: 24858312 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of potassium 2-(l-hydroxypentyl)-benzoate on hippocampal neurons, synapses and dystrophic axons in APP/PS1 mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Sep;236(9):2761-2771. doi: 10.1007/s00213-019-05251-x. Epub 2019 Jun 4. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 31165206
-
The attenuation effect of potassium 2-(1-hydroxypentyl)-benzoate in a mouse model of diabetes-associated cognitive decline: The protein expression in the brain.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022 Jul;28(7):1108-1123. doi: 10.1111/cns.13847. Epub 2022 Apr 20. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022. PMID: 35445545 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Modeling of Alzheimer's Disease.Front Neurosci. 2022 Mar 31;16:807473. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.807473. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35431779 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

