This is a preprint.
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1E: Clinical Natural History and Molecular Impact of PMP22 Variants
- PMID: 40343019
- PMCID: PMC12060940
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.05.01.25326605
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1E: Clinical Natural History and Molecular Impact of PMP22 Variants
Update in
-
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1E: clinical natural history and molecular impact of PMP22 variants.Brain. 2025 Jun 9:awaf219. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaf219. Online ahead of print. Brain. 2025. PMID: 40488457
Abstract
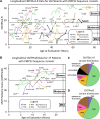
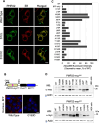
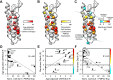
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1E (CMT1E) is a rare, autosomal dominant peripheral neuropathy caused by missense variants, deletions, and truncations within the peripheral myelin protein-22 (PMP22) gene. CMT1E phenotypes vary depending on the specific variant, ranging from mild to severe, and there is little natural history and phenotypic progression data on individuals with CMT1E. Patients with CMT1E were evaluated during initial and follow-up visits at sites within the Inherited Neuropathy Consortium. Clinical characteristics were obtained from history, neurological exams, and nerve conduction studies. Clinical outcome measures were used to quantify baseline and longitudinal changes, including the Rasch-modified CMT Examination Score version 2 (CMTESv2-R) and the CMT Pediatric Scale (CMTPedS). The trafficking of PMP22 variants in transfected cells was correlated to disease severity. Twenty-four, presumed disease-causing PMP22 variants were identified in 50 individuals from 35 families, including 19 missense variants, three in-frame deletions, and two truncations. Twenty-nine patients presented with delayed walking during childhood. At their baseline evaluation, the mean CMTESv2-R in 46 patients was 16 ± 7.72 (out of 32), and the mean CMTPedS from 17 patients was 28 ± 6.35 (out of 44). Six individuals presented with hearing loss, eleven with scoliosis, three with hip dysplasia, and one with both scoliosis and hip dysplasia. Twenty variants were localized within in transmembrane domains; 31 of 35 individuals with these variants had moderate to severe phenotypes. Three variants were found in the extracellular domain and were associated with milder phenotypes. Reduced expression of PMP22 at the cell surface, and the location of missense variants within in the transmembrane domain correlated with disease severity. Pathogenic PMP22 variants located within the transmembrane regions usually cause a moderate to severe clinical phenotype, beginning in early childhood, and have impaired trafficking to the plasma membrane.
Keywords: Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1E (CMT1E); PMP22; natural history.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Skre H. Genetic and clinical aspects of Charcot-Marie-Tooth’s disease. Clinical genetics 1974;6:98–118. - PubMed
-
- Lupski JR, de Oca-Luna RM, Slaugenhaupt S, et al. DNA duplication associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A. Cell 1991;66:219–232. - PubMed
-
- Raeymaekers P, Timmerman V, Nelis E, et al. Duplication in chromosome 17p11.2 in Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 1a (CMT 1a). The HMSN Collaborative Research Group. Neuromuscular disorders : NMD 1991;1:93–97. - PubMed
-
- Chance PF, Alderson MK, Leppig KA, et al. DNA deletion associated with hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies. Cell 1993;72:143–151. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
