Berberine hydrochloride-loaded liposomes-in-hydrogel microneedles achieve the efficient treatment for psoriasis
- PMID: 40343170
- PMCID: PMC12059721
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101795
Berberine hydrochloride-loaded liposomes-in-hydrogel microneedles achieve the efficient treatment for psoriasis
Abstract
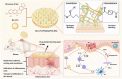
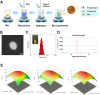
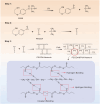
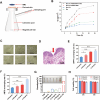
Psoriasis is a common immune-mediated squamous skin disease, primarily characterized by the over proliferation of keratinocytes and a significant thickening of the stratum corneum. Traditional systemic drug delivery therapies often fall short due to low drug bioavailability and significant toxic side effects. Topical medications, while capable of achieving local or systemic treatment via transdermal routes, face limitations in psoriasis patients due to the abnormal thickening of the epidermis, which reduces skin permeability and hampers drug penetration efficiency. Hydrogel microneedles, as an emerging transdermal drug delivery technology, offer significant advantages such as high permeability, ease of use, low toxicity and side effects, and controlled release. Therefore, this study developed a liposome-hydrogel microneedle delivery system for the administration of berberine hydrochloride. We successfully prepared berberine hydrochloride-loaded liposomes (Ber-LPs) with high encapsulation efficiency and good stability, and integrated them into hydrogel microneedles crosslinked with PVA and PEGDA (Ber-LPs-PEGDA&PVA MNs) through a photocuring method. These microneedles exhibit an intact structure, high mechanical strength, and effective skin penetration. In vivo studies on anti-psoriatic effects showed that, compared to the model group, Ber-LPs-PEGDA&PVA MNs significantly alleviated imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like symptoms in mice, reduced skin epidermal thickness, decreased the expression levels of inflammatory cytokines, and lowered the expression of CD31 and VEGF, demonstrating excellent therapeutic efficacy. Additionally, the microneedles exhibited good drug release properties, antioxidant capacity, and biocompatibility. The novel hydrogel microneedle drug delivery system developed in this study offers a safe and effective solution for the treatment of psoriasis, with significant potential for clinical application.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Hydrogel microneedles; Inflammatory skin diseases; Liposomes; Psoriasis.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Microneedle system carrying Momordin Ic-loaded ROS-responsive hydrogel ameliorates psoriasis via targeted anti-inflammatory and reactive oxygen species (ROS)-scavenging mechanisms.Int J Pharm. 2025 May 15;676:125530. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125530. Epub 2025 Apr 6. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40199433
-
Screening and preparation of curcumin nano-formulations combined with dissolving microneedles on the application in the effective treatment of psoriasis.Int J Pharm. 2025 Apr 30;675:125528. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125528. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40157563
-
A Novel Methacryloyl Chitosan Hydrogel Microneedles Patch with Sustainable Drug Release Property for Effective Treatment of Psoriasis.Macromol Biosci. 2023 Dec;23(12):e2300194. doi: 10.1002/mabi.202300194. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Macromol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37534769
-
Potential strategy of microneedle-based transdermal drug delivery system for effective management of skin-related immune disorders.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2024 Feb;195:114148. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2023.11.013. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2024. PMID: 37995878 Review.
-
Microneedle-mediated transdermal drug delivery for treating diverse skin diseases.Acta Biomater. 2021 Feb;121:119-133. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.12.004. Epub 2020 Dec 5. Acta Biomater. 2021. PMID: 33285323 Review.
References
-
- Griffiths C.E.M., Armstrong A.W., Gudjonsson J.E., Barker J. Psoriasis. Lancet. 2021;397(10281):1301–1315. - PubMed
-
- Perry M. Psoriasis: an overview. Br. J. Nurs. 2024;33(15):686–692. - PubMed
-
- Sobolev V., Muminova M., Zhukova O., Denisova E., Soboleva A., Potekaev N., Korsunskaya I., Mezentsev A. HGF, HNRPD, and sFLT1 interfere with the induction of VEGF in patients with severe psoriasis. Curr. Mol. Med. 2024;24 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

