Deciphering the role of traditional flipping crafts in medium-temperature Daqu fermentation: Microbial succession and metabolic phenotypes
- PMID: 40343192
- PMCID: PMC12059395
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2025.101063
Deciphering the role of traditional flipping crafts in medium-temperature Daqu fermentation: Microbial succession and metabolic phenotypes
Abstract
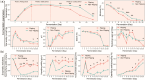
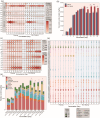
Medium-temperature Daqu (MTD) serves as the saccharification and fermentation starter for Nongxiangxing Baijiu. Flipping Daqu (FD) during fermentation is a key craft in traditional MTD preparation. However, the mechanism underlying this flipping craft remains unclear. To address this, we systematically compared FD with non-flipping Daqu (NFD) to elucidate microbial succession dynamics, metabolic phenotypes, and environmental drivers. Our results demonstrated divergent microbial community succession patterns between FD and NFD during the stable fermentation phase (days 9-25). FD exhibited significantly higher enzyme activities and volatile ketone content, along with lower core temperatures compared to NFD. Metabolite production in FD was influenced by both bacteria and fungi, whereas fungi predominantly controlled metabolite production in NFD. Co-occurrence network analysis revealed that the microbial community in FD was simpler yet more stable compared to that in NFD. Microbial succession in MTD was primarily driven by interspecies interactions and environmental factors. Furthermore, deterministic processes and stochastic processes jointly governed microbial assembly both FD and NFD, with temperature, moisture, and acidity as the key driving factors. These findings highlight the pivotal role of the flipping crafts in enhancing microbial functionality and metabolic diversity, offering a theoretical basis for optimizing MTD production and advancing intelligent fermentation systems.
Keywords: Driving factors; Medium-temperature Daqu; Metabolic phenotypes; Microecology; Traditional flipping crafts.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Chen J., Nan J., Xu D., Mo L., Zheng Y., Chao L., Qu H., Guo Y., Li F., Bao Y. Response differences between soil fungal and bacterial communities under opencast coal mining disturbance conditions. Catena. 2020;194 doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104779. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

