Macrophage-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: A Novel Therapeutic Alternative for Diabetic Wound
- PMID: 40343196
- PMCID: PMC12060905
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S518655
Macrophage-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: A Novel Therapeutic Alternative for Diabetic Wound
Abstract
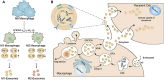
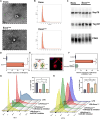
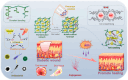
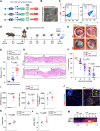
Diabetic wounds represent a significant clinical and economic challenge owing to their chronicity and susceptibility to complications. Dysregulated macrophage function is a key factor in delayed wound healing. Recent studies have emphasized the therapeutic potential of macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles (MDEVs), which are enriched with bioactive molecules such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids that mirror the state of their parent cells. MDEVs influence immune modulation, angiogenesis, extracellular matrix remodeling, and intercellular communication. In this review, we summarize and discuss the biological properties and therapeutic mechanisms of MDEVs in diabetic wound healing, highlighting strategies to enhance their efficacy through bioengineering and advanced delivery systems. We also explore the integration of MDEVs into innovative wound care technologies. Addressing current limitations and advancing clinical translation of MDEVs could advance diabetic wound management, offering a precise, effective, and versatile therapeutic option.
Keywords: diabetic wound; extracellular vesicle; macrophage; nanomedicine; therapy.
© 2025 Shi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

