The oxidative-stress-senescence axis in keratoconus: new insights into corneal degeneration
- PMID: 40343259
- PMCID: PMC12058492
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1539542
The oxidative-stress-senescence axis in keratoconus: new insights into corneal degeneration
Abstract
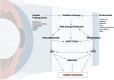
Keratoconus is a bilateral and asymmetric degenerative eye disease that causes corneal thinning and bowing, leading to irregular astigmatism and vision loss. Although environmental and genetic factors contribute to the disease's development, the exact cause and underlying pathological mechanism remain unknown. In this review, we comprehensively explore the latest pathophysiological mechanisms of keratoconus, focusing on oxidative damage and inflammation. Senescence emerges as a key driver of keratoconus pathogenesis. Understanding these common elements enhances our understanding of the disease and paves the way for innovative therapeutic approaches to keratoconus.
Keywords: antioxidant therapy; inflammation; keratoconus; mitochondrial dysfunction; oxidative stress; senescence.
Copyright © 2025 Passaro, Rinaldi, Morgera, Feola, Romano, Troisi, Strianese, Piscopo, Messina, Romano, Porcellini, Pezone and Costagliola.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
-
- Asimellis G., Kaufman E. J. (2024). Keratoconus. StatPearls. Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470435/ (Accessed June 10, 2024). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

