Evaluating ginkgetin from Ginkgo biloba as a novel agent for sleep promotion through molecular docking and in vivo studies
- PMID: 40343295
- PMCID: PMC12057750
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2025.82718.17878
Evaluating ginkgetin from Ginkgo biloba as a novel agent for sleep promotion through molecular docking and in vivo studies
Abstract
Objectives: Sleep impacts the well-being and quality of life of millions. Given conventional pharmacotherapy's limitations and side effects, the quest for adequate and proper sleep promotion is imperative. This study aims to identify a suitable and effective compound for sleep by examining qualified herbal compounds in the PubChem database using in silico methods. Ultimately, the extracted compound (ginkgetin, a bioactive flavonoid from Ginkgo biloba) through molecular docking by considering the GABAA receptors will be evaluated through the in vivo method in an animal model to serve as proof for the findings from the molecular docking process.
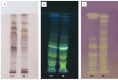
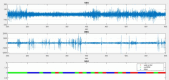
Materials and methods: Utilizing a comprehensive approach, this research employed molecular docking to screen 2299 phytochemicals for their affinity towards the GABAA receptor, focusing on the GABA, benzodiazepine, and steroid-binding sites. Ginkgetin emerged as a top candidate due to its high binding affinity. Subsequent in vivo electrophysiological assessments in rats treated with G. biloba extract containing ginkgetin evaluated alterations in sleep architecture, REM, and NREM sleep phases.
Results: Molecular docking identified ginkgetin as possessing the highest binding affinity among the screened phytochemicals. In vivo studies corroborated these findings, demonstrating that rats treated with Ginkgo biloba extract significantly enhanced REM and NREM sleep compared to controls.
Conclusion: Ginkgetin, derived from G. biloba, shows promising potential as a novel therapeutic agent for sleep disorders, supported by its strong affinity to key receptor sites and its efficacy in modulating sleep architecture in vivo. These findings contribute to the expanding evidence base for the therapeutic use of G. biloba in sleep promotion and underscore the need for further research to elucidate the mechanisms and clinical applicability of ginkgetin in sleep disorder treatment.
Keywords: GABAA receptor; Ginkgetin; Ginkgo biloba; Molecular docking; Sleep.
© 2025. This work is openly licensed via CC BY 4.0.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Therapeutic effect of ginkgetin on smoke-induced airway inflammation by down-regulating the c/EBPβ signaling pathway and CCL2 expression.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Sep 15;331:118284. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118284. Epub 2024 May 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38735420
-
Ginkgetin derived from Ginkgo biloba leaves enhances the therapeutic effect of cisplatin via ferroptosis-mediated disruption of the Nrf2/HO-1 axis in EGFR wild-type non-small-cell lung cancer.Phytomedicine. 2021 Jan;80:153370. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153370. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33113504
-
Ginkgetin Alleviates Inflammation and Senescence by Targeting STING.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jan;12(2):e2407222. doi: 10.1002/advs.202407222. Epub 2024 Nov 19. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39558862 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Potential of Biflavone Ginkgetin: A Review.Life (Basel). 2023 Feb 16;13(2):562. doi: 10.3390/life13020562. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biflavonoids: Important Contributions to the Health Benefits of Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba L.).Plants (Basel). 2022 May 23;11(10):1381. doi: 10.3390/plants11101381. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631806 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Simeone TA, Donevan SD, Rho JM. Molecular biology and ontogeny of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors in the mammalian central nervous system. J Child Neurol. 2003;18:39–48. - PubMed
-
- Koche D, Shirsat R, Kawale M. An overerview of major classes of phytochemicals: their types and role in disease prevention. Hislopia J. 2016;9:1–11.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
