Advances in basic biology of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.): a comprehensive overview
- PMID: 40343348
- PMCID: PMC12058308
- DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhaf081
Advances in basic biology of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.): a comprehensive overview
Abstract
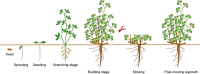
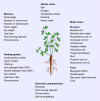
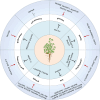
Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.), a perennial legume forage, has been broadly cultivated owing to a variety of favorable characteristics, including comprehensive ecological adaptability, superior nutritive value and palatability, and nitrogen fixation capacity. The productivity traits of alfalfa, specifically its biomass yield and forage quality, are significantly influenced by a series of determinants, including internal developmental factors and external environmental cues. However, the regulatory mechanisms underlying the fundamental biological problems of alfalfa remain elusive. Here, we conducted a comprehensive review focusing on the genomics of alfalfa, advancements in gene-editing technologies, and the identification of genes that control pivotal agronomic characteristics, including biomass formation, nutritional quality, flowering time, and resistance to various stresses. Moreover, a molecular design roadmap for the 'ideal alfalfa' has been proposed and the potential of pangenomes, self-incompatibility mechanisms, de novo domestication, and intelligent breeding strategies to enhance alfalfa's yield, quality, and resilience were further discussed. This review will provide comprehensive information on the basic biology of alfalfa and offer new insights for the cultivation of ideal alfalfa.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nanjing Agricultural University.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Singer SD, Hannoufa A, Acharya S. Molecular improvement of alfalfa for enhanced productivity and adaptability in a changing environment. Plant Cell Environ. 2018;41:1955–71 - PubMed
-
- Latif A, Sun Y, Noman A. Herbaceous alfalfa plant as a multipurpose crop and predominant forage specie in Pakistan. Front Sustain Food Syst. 2023;7:1126151
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

