Population structure and genetic diversity of Mi pigs based on SINE-RIPs
- PMID: 40343362
- PMCID: PMC12058712
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1500115
Population structure and genetic diversity of Mi pigs based on SINE-RIPs
Abstract
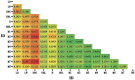
Mi pigs, a Chinese native breed found in Jintan and Yangzhong in Jiangsu Province, were recorded as having only a few hundred members in the latest national livestock and poultry genetic resources survey. To explore their conservation and breeding prospects, 18 SINE Retrotransposon Insertion Polymorphisms (sine-rips) were analyzed using PCR to assess the population structure and genetic diversity of Mi pigs. These pigs were grouped into eight families based on a UPGMA phylogenetic tree. The genetic distances between the Mi pig populations and commercial breeds ranged from 0.3712 to 0.7609, indicating significant divergence. Conversely, they showed a closer genetic relationship with other local Jiangsu breeds, with distances varying from 0.0943 to 0.6122, a finding supported by the UPGMA tree. The populations displayed a substantial degree of outbreeding, with Fis values from -0.4744 (M5) to -0.0847 (M8) and Fst values from 0.0534 (M3, M8) to 0.2265 (M2, M7), highlighting their genetic diversity which is crucial for the conservation of Mi pigs. Despite this diversity, the population sizes were uneven, with M5, M7, and M8 having 6, 5, and 7 individuals, respectively. These findings lay a theoretical foundation for the ongoing conservation and breeding efforts for Mi pigs.
Keywords: Mi pig; SINE; genetic diversity; population structure; retrotransposon insertion polymorphisms.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Zhou, Zheng, Yu, He, Chen, Qiao, Moawad, Tian, Li and Song.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Zhang X. Comparison on partial traits and investigation on breed Resourses of Huai Bei Pig in Gan Yu region [Master].Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University. (2004).
-
- Cao HFHH, Chen JF, Jin WM, Zheng QW. Mi Pig. Animal Husbandry Vet Med. (1988) 2:63–5.
-
- Jiajin Chen GZ, Li Q. Research on the history and characteristics of germplasm resource of red lantern Pig. Ancient Modern Agricul. (2016) 4:68–79.
-
- Chang Q, Zhou KY, Wang YQ, Zhang ZK, Cao X. Rapd analysis of genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationship of the Taihu pigs. Yi Chuan Xue Bao. (1999) 26:480–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

