Global pharmacovigilance reporting of the first monoclonal antibody for canine osteoarthritis: a case study with bedinvetmab (Librela™)
- PMID: 40343372
- PMCID: PMC12061024
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1558222
Global pharmacovigilance reporting of the first monoclonal antibody for canine osteoarthritis: a case study with bedinvetmab (Librela™)
Abstract
Introduction: Continuous product monitoring post approval builds on the knowledge gained during clinical studies to aid in understanding a product's safety and efficacy profile. Pharmacovigilance reporting of a medicinal product might be influenced by several factors including duration in the market, geographical region and veterinary practices. The goals of this report are to present the global data accrued for bedinvetmab, the first monoclonal antibody for canine osteoarthritis, and to explore reporting patterns globally and across major markets.
Methods: Adverse event reports from the Zoetis Global Pharmacovigilance database (from first introduction on 01 February 2021 through 30 June 2024) were collected irrespective of suspected causality or off-label use. Each adverse event was coded using the Veterinary Dictionary for Drug Related Affairs (VeDDRA) terminology. The top 20 most reported VeDDRA terms were identified. Countries were ranked by number of doses distributed and frequency of adverse events.
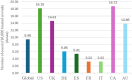
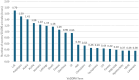
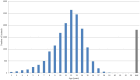
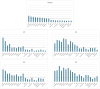
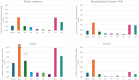
Results: Globally, 18,102,535 doses of bedinvetmab were sold during the study period with a total of 17,162 adverse events reported in dogs (9.48 events/10,000 treated animals (doses)). Eight clinical signs were considered rare (1-10 events/10,000 treated animals (doses)) with lack of efficacy having the highest rate (1.70) followed by polydipsia, ataxia, polyuria/pollakiuria, anorexia, lethargy, death, and emesis. All other clinical signs were considered very rare (< 1 event/10,000 treated animals (doses)). Median (interquartile range) of dogs' age and body weight were 12 (10-13) years and 26 (16-34.6) kg, respectively. The top eight countries by market size were United States (US), United Kingdom (UK), Germany, Spain, France, Italy, Canada, and Australia; from these, the top five by frequency of adverse events were Canada, US, UK, Australia and Germany. The most reported adverse events following bedinvetmab are considered rare or very rare.
Discussion: The reported clinical signs generally aligned with expected adverse events or were anticipated within the population receiving bedinvetmab. Reporting rates and patterns in general and for specific VeDDRA terms greatly varied between countries and were not related to market size. Most dogs for which adverse events were reported were considered older and in fair clinical condition. Reporting to pharmacovigilance contributes to the understanding of the safety profile of a medicinal product.
Keywords: bedinvetmab; canine; chronic pain; dogs; nerve growth factor; osteoarthritis; pharmacovigilance; safety.
Copyright © 2025 Monteiro, Simon, Knesl, Mandello, Nederveld, Olby, Innes and Lascelles.
Conflict of interest statement
BM, TS, OK, KM and SN were employed by Zoetis. DL, NO and JI were consultants to Zoetis. The authors declare that this study received funding from Zoetis. The funder had the following involvement in the study: study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article, and the decision to submit it for publication. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

